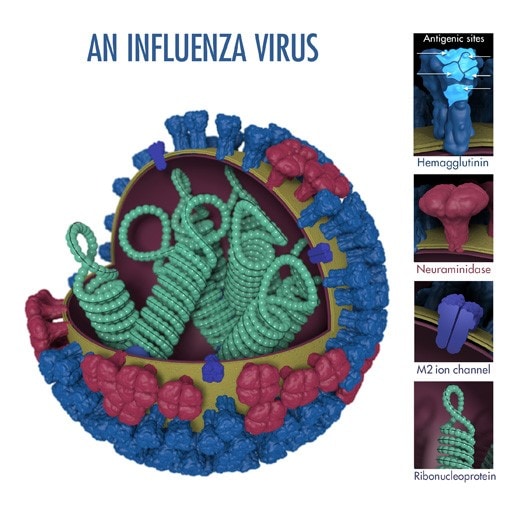
An influenza virus’ surface proteins: hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) are “antigens,” which are molecular structures that trigger an immune response in an infected host. The term “antigenic properties” is used to describe the characteristics of the immune response triggered by the antigens of a particular virus. “Antigenic characterization” refers to the analysis of different viruses’ antigenic properties to help determine their similarity. Flu experts attempt to choose vaccine viruses for inclusion in seasonal flu vaccines that are antigenically similar or closely “matched” to the viruses most likely to spread and cause illness during the flu season.
CDC Study Shows Potential to Improve Flu Vaccine Strain Selection
A recent study describes CDC's development and use of a new lab test that can more quickly and accurately characterize circulating flu A(H3N2) viruses, which evolve more rapidly than other flu subtypes. This new method is a major step forward in overcoming the challenges of vaccine strain selection and how well flu vaccines work against flu viruses.
| Learn More |





















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario