QuickStats: Percentage* of Residential Care Community Residents with an Advance Directive,† by Census Division§ — National Study of Long-Term Care Providers, 2016
Weekly / July 20, 2018 / 67(28);790
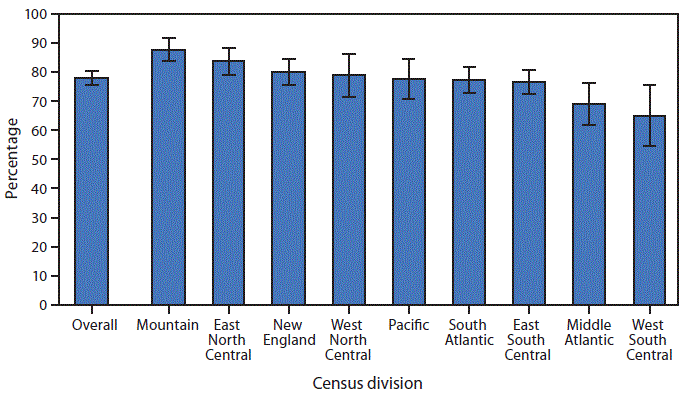
* With 95% confidence intervals shown with error bars.
† Based on the question “Of the current residents, how many have documentation of an advance directive in their file?” asked of the 98% of communities that responded “yes” to “Does this residential care community typically maintain documentation of residents’ advance directives or have documentation that an advance directive exists in resident files?”
§ New England: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont; Middle Atlantic: New Jersey, New York, and Pennsylvania; East North Central: Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin; West North Central: Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota; South Atlantic: Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, District of Columbia, and West Virginia; East South Central: Alabama, Kentucky, Mississippi, and Tennessee; West South Central: Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas; Mountain: Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming; Pacific: Alaska, California, Hawaii, Oregon, and Washington.
In 2016, 77.9% of residents in residential care communities had an advance directive documented in their files. By Census division, the highest percentage (87.8%) of residents who had an advance directive were located in the Mountain division, followed by residents in East North Central (83.7%), New England (80.0%), West North Central (78.9%), Pacific (77.6%), South Atlantic (77.4%), East South Central (76.4%), Middle Atlantic (68.8%), and West South Central (64.9%).
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, National Study of Long-Term Care Providers, 2016. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nsltcp/index.htm.
Reported by: Jessica Penn Lendon, PhD, jlendon@cdc.gov, 301-458-4714; Christine Caffrey, PhD; Denys T. Lau, PhD.






















.png)
.png)











No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario