
Eczema Triggers
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic, non-infectious, inflammatory skin disease, which causes skin reddening and itching. It is usually very common in children; but, it can affect individuals at any age.
It has a tendency to flare-up periodically and generally become worse at night. The main symptoms of eczema include itching, redness and dry, skin. It may occasionally results in blister formation, which may leak fluids when scratched. As the disease persists for a long period, the skin may eventually become thick, cracked, and swollen.
The intensity of these skin symptoms varies from individual to individual. Depending upon the age, the site of eczema differs, like cheeks, arm and legs are more common site in case of infants, whereas in adolescent and adults have eczema at the back of neck, and knee, inside the elbow joints, palm and feet, but rarely affects their face.
Although there is practically no cure for eczema, the symptoms can be subsided to a greater extend by regularly moisturizing the skin, applying medicated creams or ointments, and avoiding harsh soaps and irritants. Beside these, some dietary management and lifestyle measure also recommended to control eczema, which are triggered by food and inhalant allergen.
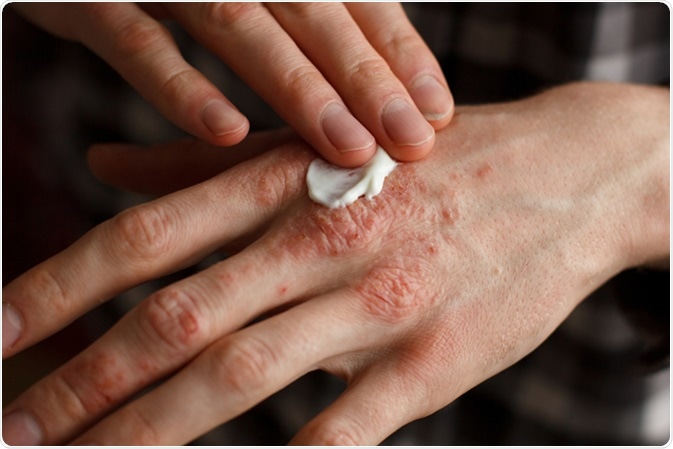
Eczema. Image Credit: Ternavskaia Olga Alibec / Shutterstock
Causes of Eczema
Although the exact cause of eczema is still not known. In eczema patients, it has been noticeable that corneal layer of the skin become damaged due to inflammatory response, which may induce by different allergen or hyper-responsiveness of immune system. This can cause insufficient protection to the inner layer of the skin.
Eczema may be developed by gene mutation that inhibits the production of filaggrin, a protein which is necessary for the formation of skin’s outer layer. As a result, skin tends to lose a lot of moistures and also become less protective against irritants, allergens, and infectious agents. A hyperactive immune system is a common feature in eczema patients. Their immune system reacts to various internal and external substances and produces antibody as a part of defense mechanism. This phenomenon triggers inflammatory reactions, which subsequently result in red, itchy, and painful skin.
Eczema Triggers
Eczema triggers can be anything that either develops eczema on the skin or intensifies already existing eczema. Eczema triggers may vary from person to person and can also change over time for a particular person.
Some common factors that can trigger eczema include:
Dry Skin
Since dry skin is one of the common features of eczema, anything that makes the skin dry can be a trigger. It may range from extreme cold or hot environment with low humidity to frequent use of harsh soaps without applying moisturizer.
Stress
Emotional stresses, such as anger, sorrow, embarrassments, anxiety, and other strong emotions, are considered as significant eczema triggers. Studies have also shown significant association between depression and eczema flare.
Irritants
Some daily life commodities that are used directly on the skin or in the house, such as body soap, shampoo, laundry soap, dish cleaning detergent, and disinfectant, can potentially trigger eczema flare. Some common examples of irritants are:
- Soaps, shampoos, and domestic cleaners
- Certain fabrics, such as woolen and synthetic cloth
- Some dietary items like cow milk, soy-products, nuts, egg ttc.
Environmental factors
Eczema patients are highly sensitive about their surrounding environment. Tobacco smoking and house dust mites increase sensitivity reaction and trigger eczema. Apart than these, pollesn, moulds, and pet fur are the other common eczema triggering factors. Even seasonal factors influence eczema. Dry and cold weather, and humid season also trigger eczema.
Sweating
Excessive sweating due to heavy exercise or wearing too many cloths can make the skin dry and trigger eczema. Sweating of some individuals can cause hyper-sensitivity reaction and trigger histamine release. Experts recommends to take shower after completion of physical exercise for individuals who have eczema to avoid sweat induce flare.
Allergens
Allergic reactions are often known to trigger skin irritation and eczema. Common food allergens that trigger eczema include milk, egg, fish, wheat, soy, and peanut. In addition, seasonal pollens, dust mites, and animal dander are among the common environmental allergens that can prompt an eczema bout.
Skin infection
Both bacterial and viral skin infections can be the potential eczema triggers. Staphylococcus aureus is a common bacterium that induces infection in eczema patients. Among viruses, herpes virus, molloscum contagiosum, and vaccinia are linked to eczema flare and can induce severe skin infections in eczema patients.
Hormones
Hormonal fluctuation in the body is sometimes known to trigger the episodes of eczema attacks, especially in women. Hormone fluctuations are common incidence during menstruation cycle, pregnancy, and at postpartum and perimenopausal phase.
Reviewed by Nita Sharma Das, PhD, ND
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0072583/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5122281/
- www.britishskinfoundation.org.uk/.../Eczema.aspx
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16911274
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/atopic-eczema/causes/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14746624
- https://atopicdermatitis.net/sweat-saliva-trigger/
- https://atopicdermatitis.net/affect-hormones/
Further Reading
Last Updated: Apr 30, 2018





















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario