
Identification of Different Types of Stem Cells
What is a Stem Cell?
Stem cells are cells that have the ability of self-renewal (synthesizing more of the same type of cell) and differentiation into other types of cells. In mammals, there are two major types of stem cells — embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells.
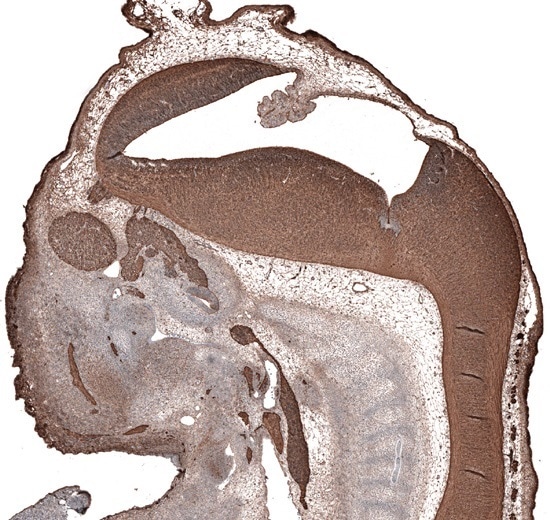
Immunohistochemical staining of mouse embryo E11 using monoclonal Anti-TUBB3 (AMAb91395) shows strong positivity in developing nervous system
Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are found in the inner mass of blastocyst early in the development. They have both self-renewal and potency properties. They are pluripotent cells, that is, they have the ability to produce an unlimited number of other types of cells.
Pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be identified by the expression of various pluripotency markers, such as SOX2, OCT4, and NANOG. These transcription factors inhibit the genes that cause differentiation and thus preserve the pluripotency of the cells.
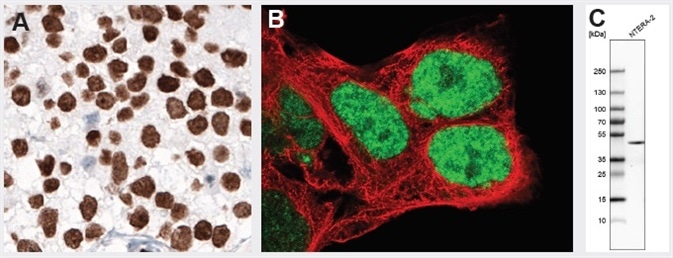
NANOG protein normally is expressed during early embryonal development and is absent in normal adult tissues. Overexpression is observed in testicular embryonal carcinoma, shown by IHC staining using monoclonal Anti-NANOG (AMAb91393). Anti-NANOG antibody AMAb91393 also shows nuclear positivity in NTERA-2 cells and band of expected size in the WB assay. NTERA-2 cells are pluripotent human embryonal carcinoma cell line, exhibiting biochemical and developmental properties similar to the cells of the early embryo.
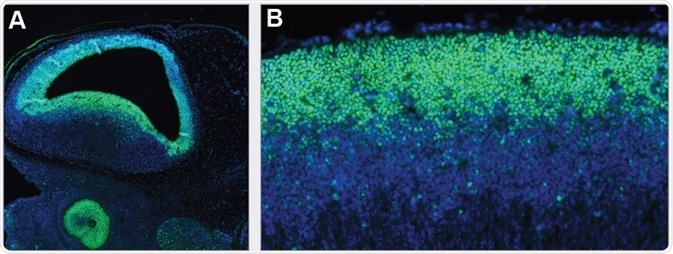
SOX2 is persistently expressed during embryonal development, first in the epiblast of preimplantation embryos, then more predominantly in the central nervous system after gastrulation. Immunohistochemical staining using monoclonal Anti-SOX2 (AMAb91307) shows nuclear positivity in the developing brain and eye (A) and neural tube (B) of mouse embryo.
At the time of embryonal development, the embryonic stem cells undergo differentiation and produce the three germ layers, namely, endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm, from which all the tissues and organs are eventually formed. For example, the ectoderm’s dorsal part gets specialized into neuroectoderm, which subsequently undergoes neurulation and encephalization and ultimately develops into the central nervous system. The neural stem cells are multipotent cells that produce different types of neural cells such as astrocytes, neurons, and oligodendrocytes in the process of neurogenesis.
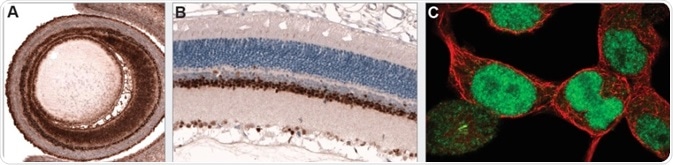
PAX6 is an essential transcription factor for overall eye development. Immunohistochemical staining using monoclonal Anti-PAX6 (AMAb91372) shows positivity in the developing eye of mouse embryo (A) and adult rat retina (B). ICC-IF staining in HEK-293 cells shows nuclear immunoreactivity.
Adult Stem Cells
Adult, or somatic, stem cells can be found in different tissues of the organism after birth. Adult stem cells are lineage-restricted (multipotent) and give rise to only the cells that represent the tissue of origin. Along with progenitor cells, they act as a repair system or might contribute to normal turnover of cells in adult tissues.
Table 1. Cell Surface Pluripotency Markers
| Gene/Protein | Catalog No | Application |
|---|---|---|
| OCT4 (POU5F1) | HPA058267 | ICC-IF |
| SOX2 | AMAb91307 | IHC, WB*, ICC-IF |
| NANOG | AMAb91393 | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
| SALL4 | HPA015791 | IHC*, ICC-IF |
| TCL1 | HPA016604 | IHC*, WB |
| NACC1 | HPA062245 | IHC, WB*, ICC-IF |
| NES | AMAb90556 | IHC, WB* |
| FUT4 (SSEA4, CD15) | AMAb91414 | WB |
*Products with enhanced validation for indicated application
Table 2. Transcription Factors
| Gene/Protein | Catalog No | Application |
|---|---|---|
| OCT4 (POU5F1) | HPA058267 | ICC-IF |
| c-MYC | HPA055893 | IHC, ICC-IF |
| SOX2 | AMAb91307 | IHC, WB*, ICC-IF |
| KLF4 | AMAb91389 | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
| SOX3 | AMAb91312 | WB |
| SOX15 | HPA067196 | IHC*, ICC-IF |
| KLF5 | HPA040398 | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
| KLF2 | HPA055964 | IHC, ICC-IF |
| NANOG | AMAb91393 | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
| TCL1 | HPA016604 | IHC, WB |
| SALL4 | HPA015791 | IHC*, ICC-IF |
| TCF3 | HPA062476 | IHC, WB |
*Products with enhanced validation for indicated application
Table 3. Induced PSCs Markers
| Gene/Protein | Catalog No | Application |
|---|---|---|
| CD13 | HPA004625 | IHC*, WB, ICC-IF |
| FUT4 (SSEA4, CD15) | AMAb91414 | WB |
| NANOG | AMAb91393 | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
*Products with enhanced validation for indicated application
Table 4. Germ Cell Markers (during specification)
| Gene/Protein | Catalog No | Application |
|---|---|---|
| PRDM1 (BLIMP1) | HPA030033 | IHC* |
| IFITM1 (Fragilis) | HPA004810 | IHC*, WB, ICC-IF |
| DAZL | HPA019777 | IHC*, WB |
| DDX4 (MVH) | HPA037764 | IHC* |
| OCT4 (POU5F1) | HPA058267 | ICC-IF |
| c-KIT (CD117) | AMAb90904 | IHC, WB |
| TEKT1 | HPA062285 | IHC |
| GDF9 | HPA069146 | IHC |
*Products with enhanced validation for indicated application
Table 5. Ectoderm and Endoderm Markers
| Gene/Protein | Catalog No | Application |
|---|---|---|
| OTX2 | HPA000633 | IHC |
| CHRD | HPA035827 | IHC |
| p63/TP73L | AMAb91224 | IHC, WB |
| PAX2 | HPA070751 | IHC*; ICC-IF |
| FOXJ3 | HPA067284 | ICC-IF |
| PAX6 | AMAb91372 | IHC, ICC-IF |
| GBX2 | HPA067809 | WB, ICC-IF |
| NES | AMAb90556 | IHC, WB* |
| TUBB3 | AMAb91395 | IHC, WB, ICC-IF |
| NOG | HPA061318 | IHC |
*Products with enhanced validation for indicated application
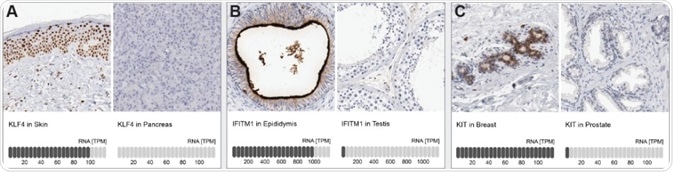
Orthogonal antibody validation: Immunohistochemical staining using polyclonal (A) Anti-KLF (HPA002926), (B) Anti-IFITM1 (HPA004810), and (C) Anti-KIT (CD-117) (HPA004471) antibodies. Note the specific expression in tissues with high RNA levels and absence of positivity in tissues with no/low RNA levels.
To find the products listed in this article, please see the Atlas Antibodies product catalog.
Atlas Antibodies
Atlas Antibodies provides the antibodies from the Human Protein Atlas. We offer a wide range of highly validated research antibodies – Triple A Polyclonals and PrecisA Monoclonals – targeting over 75% of the human proteome.
Triple A Polyclonals are primary antibodies developed and characterized within the Human Protein Altas project. The 21,000 rabbit polyclonal antibodies cover 75% of the human proteome and are validated in IHC, WB and ICC-IF. For each IHC antibody, you can explore 500 IHC images for each antibody.
PrecisA Monoclonals are primary mouse monoclonals with unique antigen design for optimal specificity. They are epitope mapped with defined specificity and isotyped for multiplexing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last updated: Oct 29, 2018 at 10:28 AM





















.png)
.png)











No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario