QuickStats: Percentage* of Residential Care Communities,† by U.S. Census Region§ — National Study of Long-Term Care Providers, 2012–2016
Weekly / November 2, 2018 / 67(43);1223
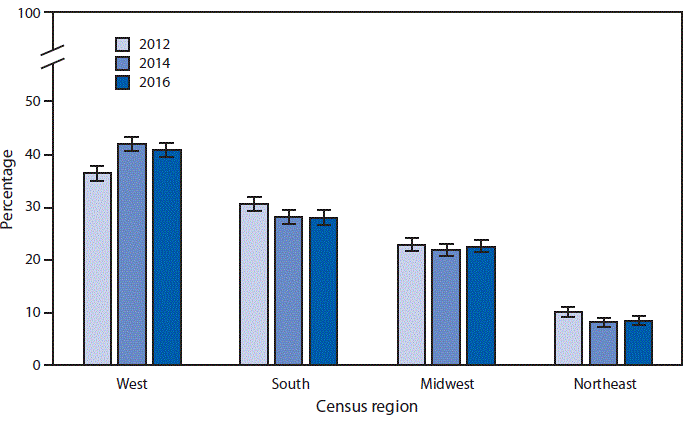
* With 95% confidence intervals indicated with error bars.
† Residential care communities include those that were state-regulated; had four or more beds; and provided room and board with at least two meals a day, around-the-clock on-site supervision, and help with personal care, such as bathing and dressing or health-related services such as medication management. Residential care communities licensed to exclusively serve the mentally ill or the intellectually or developmentally disabled populations were excluded.
§ Northeast: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont. Midwest: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, and Wisconsin. South: Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia. West: Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming.
During 2012–2016, the percentage of residential care communities located in the West increased from 36.4% to 40.8%. Throughout the period, a higher percentage of residential care communities were located in the West compared with other regions. The percentage of residential care communities declined from 30.6% in 2012 to 28% in 2016 in the South and from 10.1% to 8.6% in the Northeast. In the Midwest, the percentage was 22.9% in 2012 and 22.6% in 2016.
Source: National Study of Long-Term Care Providers, 2012–2016 data. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nsltcp/index.htm.
Reported by: Amanuel Melekin, PhD, opn1@cdc.gov; Vincent Rome, MPH.






















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario