Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Summary
This is an emerging, rapidly evolving situation and CDC will provide updated information as it becomes available, in addition to updated guidance.
Updated February 13, 2020
Background
CDC is closely monitoring an outbreak of respiratory disease caused by a novel (new) coronavirus that was first detected in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China and which continues to expand. On February 11, 2020, the World Health Organization named the disease coronavirus disease 2019 (abbreviated “COVID-19”).
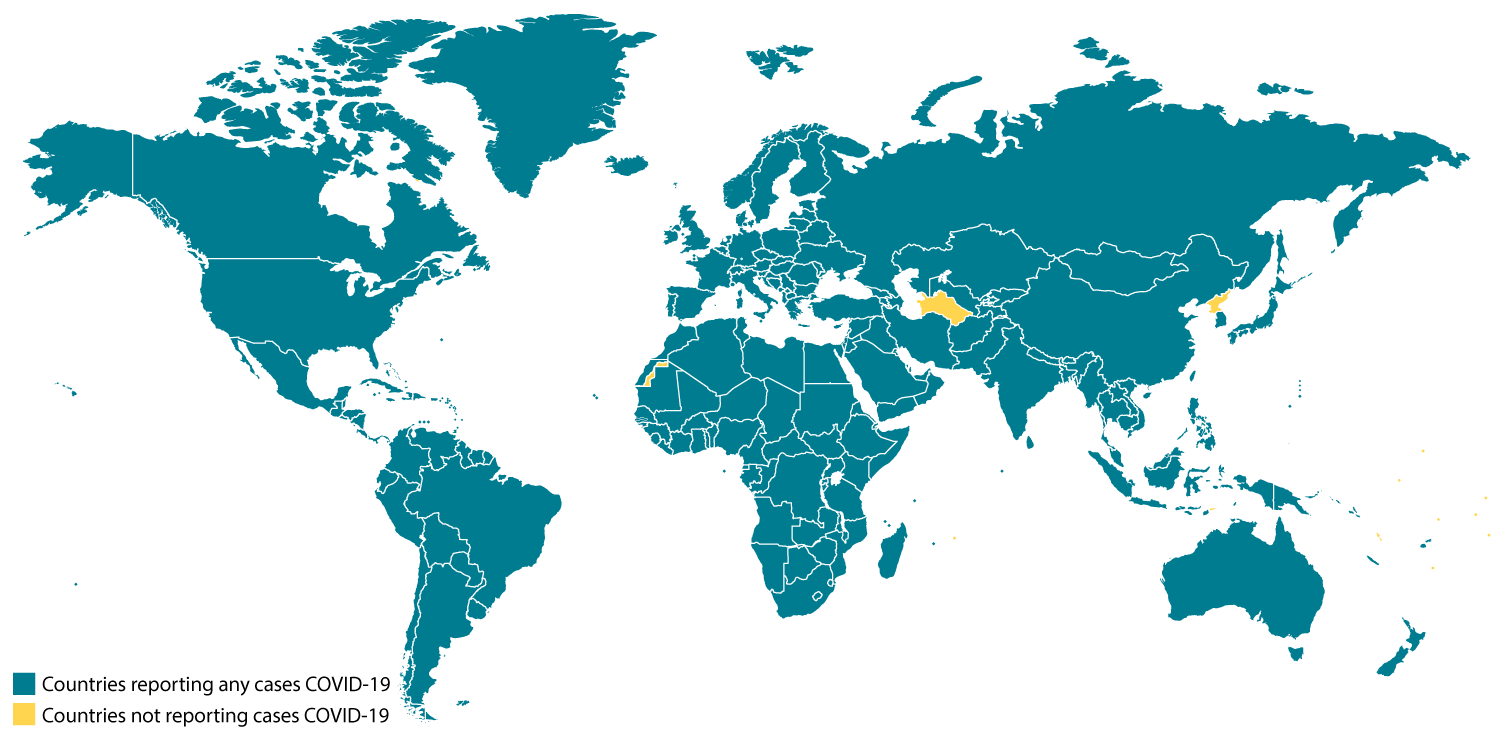
Chinese health officials have reported tens of thousands of cases of COVID-19 in China, with the virus reportedly spreading from person-to-person in parts of that country. COVID-19 illnesses, most of them associated with travel from Wuhan, also are being reported in a growing number of international locations, including the United States. Some person-to-person spread of this virus outside China has been detected. The United States reported the first confirmed instance of person-to-person spread with this virus on January 30, 2020.
On January 30, 2020, the International Health Regulations Emergency Committee of the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a “public health emergency of international concern” (PHEIC). On January 31, 2020, Health and Human Services Secretary Alex M. Azar II declared a public health emergency (PHE) for the United States to aid the nation’s healthcare community in responding to COVID-19. Also on January 31, the President of the United States signed a presidential “Proclamation on Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Persons who Pose a Risk of Transmitting 2019 Novel Coronavirus.” These measures were announced at a press briefing by members of the President’s Coronavirus Task Force.
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are common in many different species of animals, including camels, cattle, cats, and bats. Rarely, animal coronaviruses can infect people and then spread between people such as with MERS, SARS, and now with this new virus (named SARS-COV2).
Source and Spread of the Virus
Chinese health authorities were the first to post the full genome of the SARS-COV2 virus in GenBank, the NIH genetic sequence database, and in the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) portal, an action which has facilitated detection of this virus. CDC is posting the full genome of the SARS-COV2 viruses detected in U.S. patients to GenBank as sequencing is completed.
The SARS-COV2 virus is a betacoronavirus, like MERS and SARs, both of which have their origins in bats. The sequences from U.S. patients are similar to the one that China initially posted, suggesting a likely single, recent emergence of this virus from an animal reservoir.
Early on, many of the patients in the COVID-19 outbreak in Wuhan, China had some link to a large seafood and live animal market, suggesting animal-to-person spread. Later, a growing number of patients reportedly did not have exposure to animal markets, indicating person-to-person spread. Chinese officials report that sustained person-to-person spread in the community is occurring in China. Person-to-person spread has been reported outside China, including in the United States and other countries. Learn what is known about the spread of newly emerged coronaviruses.
On This Page
Confirmed COVID-19 Cases Globally
COVID-19 in the U.S.
Situation in U.S.
Imported cases of COVID-19 in travelers have been detected in the U.S. Person-to-person spread of COVID-19 also has been seen among close contacts of returned travelers from Wuhan, but at this time, this virus is NOT currently spreading in the community in the United States.
The U.S. government has taken unprecedented steps related to travel in response to the growing public health threat posed by this new coronavirus, including suspending entry in the United States of foreign nationals who have visited China within the past 14 days. Measures monitor the health of those who are allowed entry into the United States (U.S. citizens, residents and family) who have been in China within 14 days also are being implemented.
Illness Severity
Both MERS and SARS have been known to cause severe illness in people. The complete clinical picture with regard to COVID-19 is not fully understood. Reported illnesses have ranged from mild to severe, including resulting in death. Learn more about the symptoms associated with COVID-19.
There are ongoing investigations to learn more. This is a rapidly evolving situation and information will be updated as it becomes available.
Risk Assessment
Outbreaks of novel virus infections among people are always of public health concern. The risk from these outbreaks depends on characteristics of the virus, including how well it spreads between people, the severity of resulting illness, and the medical or other measures available to control the impact of the virus (for example, vaccine or treatment medications).
The potential public health threat posed by COVID-19 virus is high, both globally and to the United States. The fact that this virus has caused illness, including illness resulting in death, and sustained person-to-person spread in China is concerning. These factors meet two of the criteria of a pandemic. It’s unclear how the situation will unfold, but risk is dependent on exposure. At this time, some people will have an increased risk of infection, for example healthcare workers caring for patients with COVID-19 and other close contacts of patients with COVID-19. For the general American public, who are unlikely to be exposed to this virus, the immediate health risk from COVID-19 is considered low at this time.
What to Expect
More cases are likely to be identified in the coming days, including more cases in the United States. It’s also likely that person-to-person spread will continue to occur, including in the United States.
CDC Response

This is a picture of CDC’s laboratory test kit for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). CDC is shipping the test kits to laboratories CDC has designated as qualified, including U.S. state and local public health laboratories, Department of Defense (DOD) laboratories and select international laboratories. The test kits are bolstering global laboratory capacity for detecting 2019-nCov.
- The federal government is working closely with state, local, tribal, and territorial partners, as well as public health partners, to respond to this public health threat.
- The public health response is multi-layered, with the goal of detecting and minimizing introductions of this virus in the United States so as to reduce the spread and the impact of this virus.
- CDC established a COVID-19 Incident Management System on January 7, 2020. On January 21, 2020, CDC activated its Emergency Operations Center to better provide ongoing support to the COVID-19 response.
- On January 27, 2020, CDC issued updated travel guidance for China, recommending that travelers avoid all nonessential travel to all of the country (Level 3 Travel Health Notice).
- The U.S. government has taken unprecedented steps with respect to travel in response to the growing public health threat posed by this new coronavirus:
- Effective February 2, 2020, at 5pm, the U.S. government suspended entry of foreign nationals who have been in China within the past 14 days.
- U.S. citizens, residents, and their immediate family members who have been in Hubei province and other parts of mainland China are allowed to enter the United States, but they are subject to health monitoring and possible quarantine for up to 14 days.
- See more at: “Proclamation on Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Persons who Pose a Risk of Transmitting 2019 Novel Coronavirus”.
- CDC issued an interim Health Alert Network (HAN) Update to inform state and local health departments and healthcare professionals about this outbreak on February 1, 2020.
- On January 30, 2020, CDC published guidance for healthcare professionals on the clinical care of COVID-19 patients.
- On February 3, 2020, CDC posted guidance for assessing the potential risk for various exposures to COVID-19 and managing those people appropriately.
- CDC has deployed multidisciplinary teams to support state health departments with clinical management, contact tracing, and communications.
- CDC has worked with the Department of State, supporting the safe return of Americans who have been stranded as a result of the ongoing outbreaks of COVID-19 and related travel restrictions. CDC has worked to assess the health of passengers as they return to the United States and provided continued daily monitoring of people who are quarantined.
- CDC has developed a real time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (rRT-PCR) test that can diagnose COVID-19 in respiratory samples from clinical specimens. On January 24, 2020, CDC publicly posted the assay protocol for this test and has begun distributing these tests to states.
- CDC has been uploading the entire genome of the viruses from reported cases in the United States to GenBank as sequencing was completed.
- CDC has grown the COVID-19 virus in cell culture, which is necessary for further studies, including for additional genetic characterization. The cell-grown virus was sent to NIH’s BEI Resources Repository for use by the broad scientific community.
CDC Recommends
- While the immediate risk of this new virus to the American public is believed to be low at this time, everyone can do their part to help us respond to this emerging public health threat:
- It’s currently flu and respiratory disease season and CDC recommends getting a flu vaccine, taking everyday preventive actions to help stop the spread of germs, and taking flu antivirals if prescribed.
- If you are a healthcare provider, be on the look-out for people who recently traveled from China and have fever and respiratory symptoms.
- If you are a healthcare provider caring for a COVID-19 patient or a public health responder, please take care of yourself and follow recommended infection control procedures.
- If you have been in China or have been exposed to someone sick with COVID-19 in the last 14 days, you will face some limitations on your movement and activity. Please follow instructions during this time. Your cooperation is integral to the ongoing public health response to try to slow spread of this virus. If you develop COVID-19 symptoms, contact your healthcare provider, and tell them about your symptoms and your travel or exposure to a COVID-19 patient.
- For people who are ill with COVID-19, please follow CDC guidance on how to reduce the risk of spreading your illness to others.
Other Available Resources
The following resources are available with information on COVID-19


































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario