CRISPR Illustrated | Biomedical Beat Blog - National Institute of General Medical Sciences

You’ve probably heard news stories and other talk about CRISPR. If you’re not a scientist—well, even if you are—it can seem a bit complex. Here’s a brief recap of what it’s all about.
In 1987, scientists noticed weird, repeating sequences of DNA in bacteria. In 2002, the abbreviation CRISPR was coined to describe the genetic oddity. By 2006, it was clear that bacteria use CRISPR to defend themselves against viruses. By 2012, scientists realized that they could modify the bacterial strategy to create a
gene-editing tool. Since then, CRISPR has been used in countless laboratory studies to understand basic biology and to study whether it’s possible to correct faulty genes that cause disease. Here’s an illustration of how the technique works.
How the CRISPR System Works
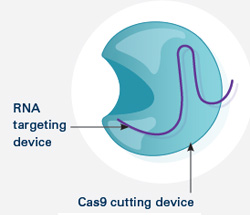
The CRISPR system has two components joined together: a finely tuned targeting device (a small strand of RNA programmed to look for a specific DNA sequence) and a strong cutting device (an enzyme called Cas9 that can cut through a double strand of DNA).
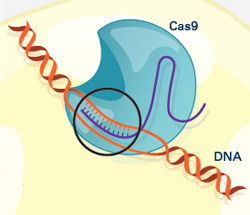
Once inside a cell, the CRISPR system locates the DNA it is programmed to find. The CRISPR seeking device recognizes and binds to the target DNA (circled, black).
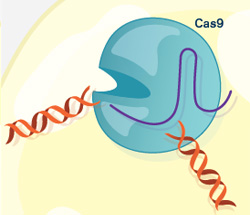
The Cas9 enzyme cuts both strands of the DNA.
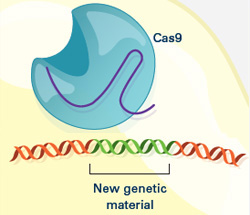
Researchers can insert into the cell new sections of DNA. The cell automatically incorporates the new DNA into the gap when it repairs the broken DNA.
CRISPR has many possible uses, including:
- Insert a new gene so the organism produces useful medicines.
- Help treat genetic diseases.
- Create tailor-made organisms to study human diseases.
- Help produce replacements for damaged or diseased tissues and organs.
























.png)
.png)











No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario