
Google AI device could predict a person’s risk of a heart attack
Google researchers along with those from its health technology subsidary Verily Life Sciences, have created a new way with which a person’s heart attack risk may be predicted. Their device looks at scans of the retina or the back layers and membranes of the eye and can then predict features such as the person’s age, his or her blood pressure and also if they smoked. These parameters could be used to predict if the person had a raised risk of heart disease or a cardiac event such as a heart attack.
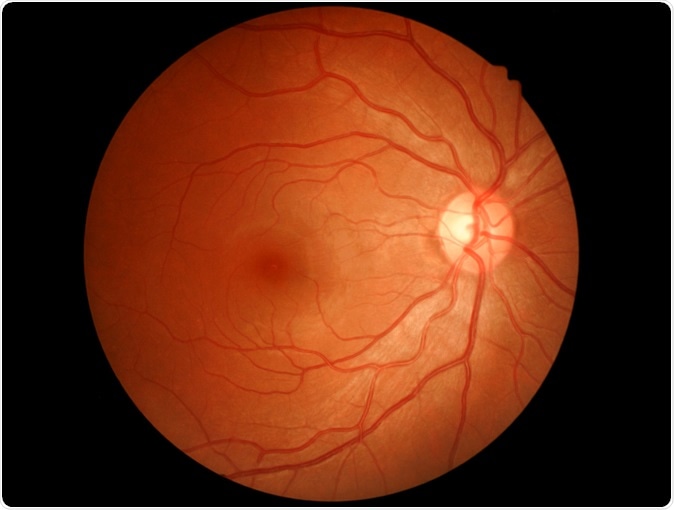
Image Credit: Memorisz / Shutterstock
According to the researchers, the algorithm that this device uses is quicker than traditional predictor tests using blood tests. This could be a useful screening tool for doctors. However the team cautions, that it is still far from being perfected for human clinical use. The study reporting the work with this device was reported in the latest issue of the Nature journal Biomedical Engineering.
Luke Oakden-Rayner, a medical researcher at the University of Adelaide, explains that AI could be used to improve upon the diagnostic tools that doctors have at hand now. He added that this should not be seen as a replacement for diagnostic tests and clinical judgement but merely an analyser that would be an extension of the diagnostic armament.
For this study the team used the machine to look into the eyes of 284,335 patients. The data was validated in two independent sets of patients comprising of 12,026 and 999 patients respectively. Apart from the retina scans they also recorded the medical data of these individuals. From the information gathered they analysed the data and checked for its predictability of a heart condition. An individual’s blood pressure, age, smoking status has been earlier reported to be analysed by merely looking at retina scans and the pattern of blood vessels therein. This is established science, the researchers add.
The machine was shown images of the retina of individuals who suffered a heart attack within five years of the study and those who did not have a cardiac event. The algorithm could predict the heart attacks and cardiovascular events, 70 percent of the time, the researchers noted. The traditional blood tests method is called the SCORE method and it can predict heart attacks with 72 percent accuracy, they report.
Experts believe that this is a credible study mainly because the science behind the hypothesis is sound. They add that it is the speed of the scans that makes the analysis lucrative. Rapid scans of the retina for example could be used as a screening tool for heart disease risk.
Google researchers hope to perfect this method and machine further so that it could analyse the present data more accurately without the aid or direction of humans. Lily Peng, a doctor and lead researcher on the project said that it was early and they were working with small data sets. In future large data sets could provide deeper insight. One of the problems with this study was that it could look at eye images at 45 degree views and this could miss out vital zones in the retina. Researchers are trying to correct this problem with new versions. Although more research is necessary, the team still calls this a major step towards “non-invasive” diagnosis and predictor of cardiovascular health.























.png)
.png)











No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario