
Campylobacter infection outbreak linked to puppies
There is a warning about a multi-state outbreak of human Campylobacter infections that seemed to have originated from the puppies sold through Petland, a national pet store chain. The warning regarding the outbreaks is being circulated by the Ohio Department of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the United States Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (USDA-APHIS). These organizations are looking into the investigation and trying to contain it.
The outbreak, as of 11th September 2017, has affected 39 people who were confirmed to be having Campylobacter infections or had symptoms that are associated with Campylobacter infection. The infections started from September 15, 2016 and continued unabated till August 12, 2017. The last case reported was on September 1, 2017. These individuals belong to 7 states including Florida, Kansas, Missouri, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, and Wisconsin.
On detailed look into the matter, it was found that all of these individuals were exposed to or in contact with puppies sold through Petland stores. Of these 39 individuals, 12 are employees of the Petland stores and 27 had recently purchased a puppy from Petland or had visited a Petland store or were part of the family that brought home a puppy from Petland. This confirms to an extent that the source of the infection could be the puppies from these stores.
Campylobacter. Pathogenic flora. The bacterium causes intestinal diseases. Symptoms of infection. Image Credit: Timonina / Shutterstock
The age range of individuals who were affected was from less than one year of age to 64 years. Median age of the affected was 22 years. Of the infected 72 percent (28 individuals) were female and 23 percent (9 individuals) had to be hospitalized as a result of the infection. Till date no deaths have occurred due to the infection.
In the laboratories, the Campylobacter isolated from the stool of the puppies from Petland as from the stool samples of those individuals affected was tested. Their DNA and genomes was sequenced to check if they came from the same source. There seemed to b a match in the strain of the microbe in both samples. Further tests are also being done. Petland is at present providing all the support and cooperation to the investigators to detect and contain the infection.
Campylobacter infection
Campylobacter is a bacterial infection that can be transmitted through dog feces of an infected dog. Spread from individual to another is rare. The CDC estimates that there are over 1.3 million cases of Campylobacter infections in people every year. Of these only one third come from animals.
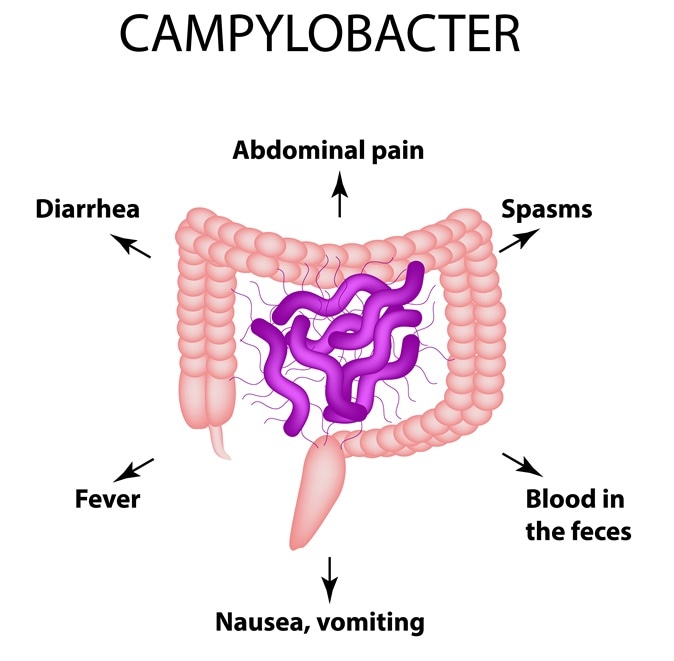
Some of the common symptoms associated with Campylobacter infection include abdominal pain, cramps, diarrhea, bloody diarrhea fever, nausea and vomiting. These symptoms appear within two to five days of exposure to the bacteria. The person is typically ill for around a week. Those with a weak immune system are prone to develop a more serious infection and this can lead to life-threatening consequences. Campylobacteriosis is more common during the summer than in winter and is one of the commonest food borne infections.
Most of the infections are caused by spiral-shaped bacteria called Campylobacter jejuni. Other species may also be involved. Diagnosis is made by microbiological examination of the stool samples of an infected person. In most individuals no treatment is required for this infection. The infection tends to resolve on its own. Extra fluids such as water, fruit juices etc. are recommended to counter dehydration and electrolyte loss due to diarrhea and vomiting. Antimicrobial therapy is necessary only for those with more severe infections. Azithromycin and ciprofloxacin are commonly used against this infection.
3d rendering - campylobacter jejuni bacteria. Image Credit: royaltystockphoto.com / Shutterstock
This infection is most commonly spread due to contamination of food and drinking water. Prevention of infection is simply by stopping all contamination from animals and birds that could be infected. Hand washing before preparation of food or after animal handling is a simple step. Poultry for example should be cooked thoroughly till all juices run clear and meat is not pink. Untreated water and unpasteurized milk should not be consumed.



































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario