Nutrire
Colon epithelial cells luminal environment and physiopathological consequences: impact of nutrition and exercise
- Received: 22 May 2017
- Accepted: 12 January 2018
- Published: 29 January 2018
Abstract
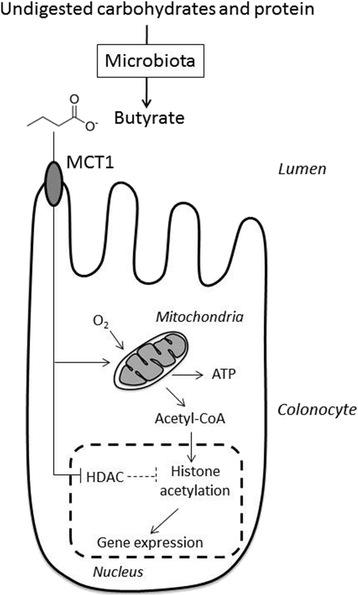
The colonic epithelial cells represent a border between the colon luminal content, containing notably bacteria and a complex mixture of compounds, and the “milieu interieur” as defined by the French physiologist Claude Bernard. The physical-chemical composition of the luminal content, including luminal pH and bacterial metabolite, that obviously is not constant, is modified for instance according to the diet. Data obtained recently indicate that physical exercise may also modify the colonic luminal content. Evidence has indicated that modification of the luminal content characteristics has, indeed, consequences for the colonic epithelial cells, notably in terms of energy metabolism and DNA integrity. Although such alterations impact presumably the homeostatic process of the colonic epithelium renewal and the epithelial barrier function, their contribution to pathological processes like mucosal inflammation, pre-neoplasia, and neoplasia remains partly elusive. Open questions remain regarding the individual and collective roles of luminal changes, particularly in a long-term perspective. These questions are related particularly to the capacity of the bacterial metabolites to cross the mucus layer before entering the colonocytes, to the concentrations of metabolites in proximity of the colonic crypt stem cells, and to the capacity of colonocytes to detoxicate deleterious compounds, to take up and utilize beneficial compounds.
Keywords
- Colon
- Intestinal microbiota
- Oxygen consumption
- DNA damage
- Barrier function
- Exercise
- Dietary protein





















.png)
.png)











No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario