01/17/2020 04:53 PM EST
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Related MedlinePlus Pages: Antibiotic Resistance
Related MedlinePlus Pages: Antibiotic Resistance
Where Antibiotic Resistance Spreads
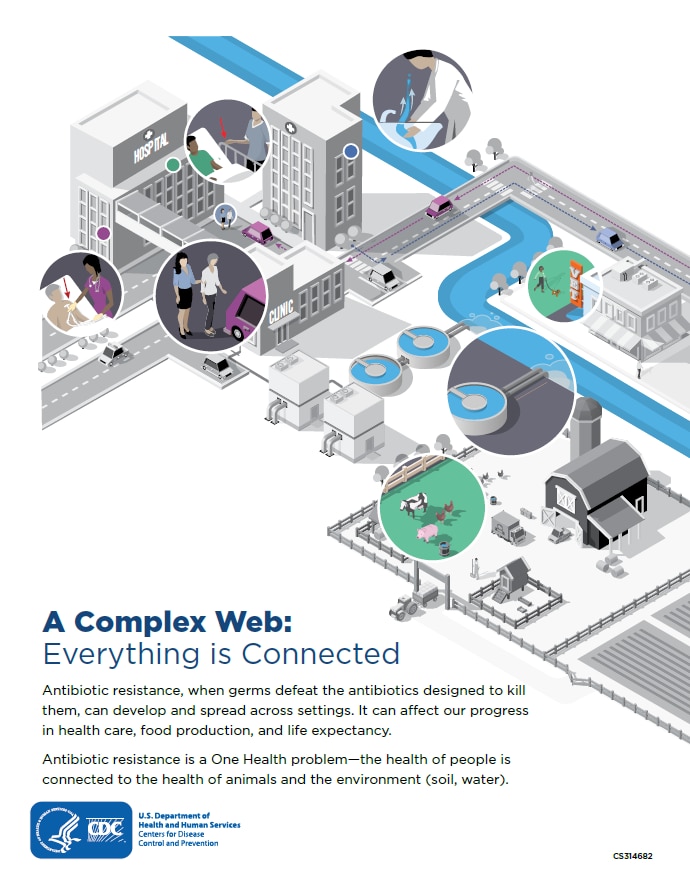
A Complex Web: Everything is Connected
Antibiotic-resistant germs can quickly spread across settings, including communities, the food supply, healthcare facilities, the environment (e.g., soil, water), and around the world. Antibiotic resistance is a One Health problem—the health of people is connected to the health of animals and the environment (soil, water).
It can affect our progress in health care, food production, and life expectancy. Antibiotic resistance is not only a U.S. problem—it is a global crisis. New forms of resistance emerge and can spread with remarkable speed between continents through people, goods, and animals.
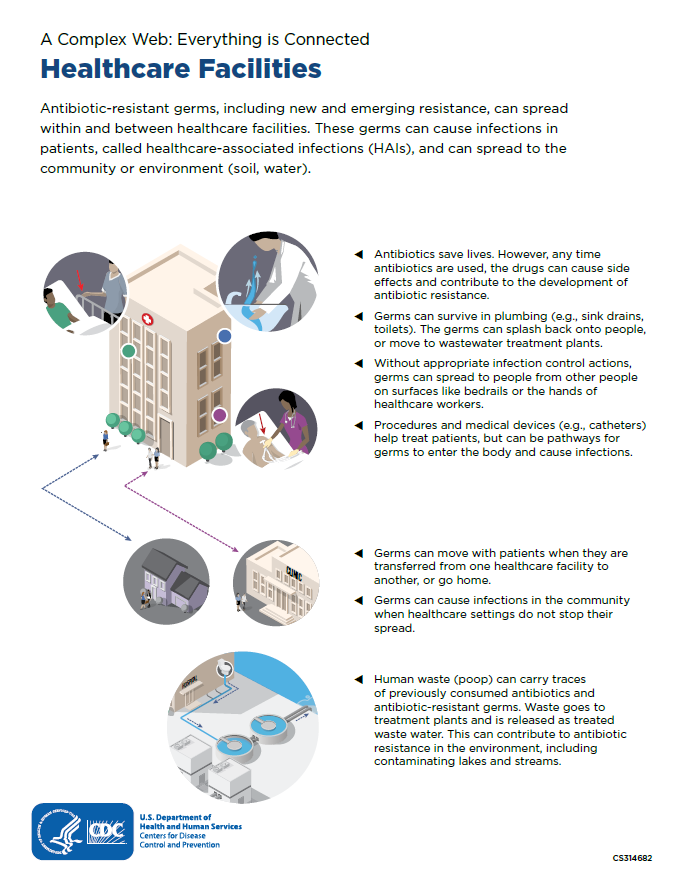
Healthcare Facilities
Antibiotic-resistant germs, including new and emerging resistance, can spread within and between healthcare facilities. These germs can cause infections in patients, called healthcare-associated infections, and can spread to the community or environment.
Community
Germs, including antibiotic-resistant germs, live and spread within our community and sometimes make people sick.
Environment
Human activity can introduce antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant germs into the environment, but it remains unclear how spread in the environment impacts human and animal health.
Food, Farms, & Animals
Animals, like people, carry germs in their gut, including antibiotic-resistant germs. The U.S. food supply is among the safest in the world, but these germs can get into the food supply and make people sick.




































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario