Cryptosporidiosis Outbreaks — United States, 2009–2017
Weekly / June 28, 2019 / 68(25);568–572
Radhika Gharpure, DVM1,2; Ariana Perez, MPH1,3; Allison D. Miller, MPH1,4; Mary E. Wikswo, MPH5; Rachel Silver, MPH1,3; Michele C. Hlavsa, MPH1 (View author affiliations)
Summary
What is already known about this topic?
Cryptosporidium is the leading cause of outbreaks of diarrhea linked to water and the third leading cause of diarrhea associated with animal contact in the United States.
What is added by this report?
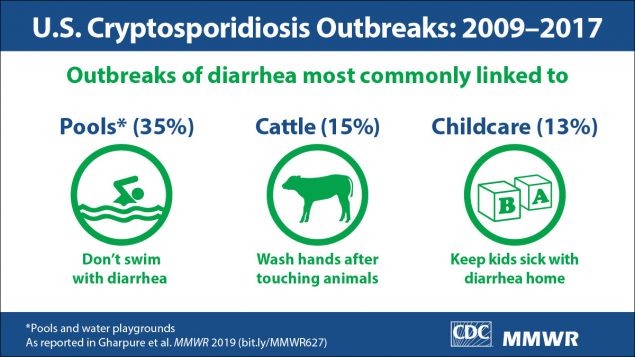
During 2009–2017, 444 cryptosporidiosis outbreaks, resulting in 7,465 cases were reported by 40 states and Puerto Rico. The number of reported outbreaks has increased an average of approximately 13% per year. Leading causes include swallowing contaminated water in pools or water playgrounds, contact with infected cattle, and contact with infected persons in child care settings.
What are the implications for public health practice?
To prevent cryptosporidiosis outbreaks, CDC recommends not swimming or attending child care if ill with diarrhea and recommends hand washing after contact with animals.





















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario