Health Matters for Women

Definition
A pregnancy-related deathis defined as the death of a woman during pregnancy or within one year of the end of pregnancy from a pregnancy complication, a chain of events initiated by pregnancy, or the aggravation of an unrelated condition by the physiologic effects of pregnancy.
Related Healthy People 2020 Objectives
MICH 5: Reduce the rate of maternal mortality.
MICH 6: Reduce maternal illness and complications due to pregnancy (complications during hospitalized labor and delivery).
MICH 7: Reduce cesarean births among low-risk (full-term, singleton, and vertex presentation) women.
MICH 10: Increase the proportion of pregnant women who receive early and adequate prenatal care.
AHS 1.1: Increase the proportion of persons with medical insurance.
Additional Information
CDC Podcasts
Listen to the latest podcasts on women’s health.
Listen to the latest podcasts on women’s health.
CDC E-Cards
Send women’s health e-cards.
Send women’s health e-cards.
Improve Black Women's Health
During African American (Black) History Month, we highlight opportunities to address issues that impact the health of black women in our communities.
Pregnancy-related mortality ratios by year and race and ethnicity: United States, 2006–2010

Source: Fig. 1. Creanga. Pregnancy-Related Mortality in the United States. Obstet Gynecol 2015.
About 650 women die each year in the United States as a result of pregnancy or delivery complications. Non-Hispanic black women have the highest risk of dying from pregnancy complications. Non-Hispanic black women have a 3.2 times higher risk of dying of pregnancy complications than non-Hispanic white women. Some maternal deaths are preventable.
What can we do to prevent pregnancy-related deaths?
For women and couples:
Take steps to adopt a healthy lifestyle and address any health problems before getting pregnant.
Start with a healthy pregnancy and get prenatal care early and throughout pregnancy.
For health providers:
Start or participate in a Perinatal Quality Collaborative. PQCs are networks of perinatal care providers and public health professionals working to improve pregnancy outcomes for women and newborns by advancing evidence-based clinical practices and processes.
Use protocols and clinical policies that are implemented systematically to reduce adverse maternal outcomes. For example, the National Partnership for Maternal Safety’s action plan provides evidence-based patient safety bundles for three conditions (obstetric hemorrhage, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and venous thromboembolism).
For health coverage:
All Health Insurance Marketplace and Medicaid plans cover pregnancy and childbirth. This is true even if pregnancy begins before coverage takes effect.
Call 1-800-311-BABY to find free or reduced cost prenatal care.
Pregnancy-related mortality ratios by age and race and ethnicity: United States, 2006–2010
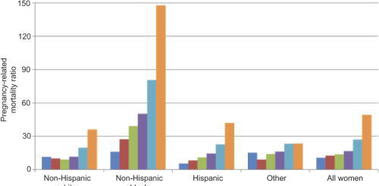
Source: Fig. 2. Creanga. Pregnancy-Related Mortality in the United States. Obstet Gynecol 2015.






















.png)











No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario