Volume 27, Number 1—January 2021
Research Letter
Waning Antibody Responses in Asymptomatic and Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection
On This Page
Figures
Downloads
Altmetric
Pyoeng Gyun Choe1, Chang Kyung Kang1, Hyeon Jeong Suh, Jongtak Jung, Kyoung-Ho Song, Ji Hwan Bang, Eu Suk Kim, Hong Bin Kim, Sang Won Park, Nam Joong Kim, Wan Beom Park , and Myoung-don Oh
, and Myoung-don Oh
Abstract
We investigated the kinetics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 neutralizing antibodies in 7 asymptomatic persons and 11 patients with pneumonia. The geometric mean titer of neutralizing antibodies declined from 219.4 at 2 months to 143.7 at 5 months after infection, indicating a waning antibody response.
Neutralizing antibodies develop in asymptomatic persons with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection; however, the initial immune response is not as strong as in patients with more severe disease (1,2). We investigated the kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies during the 5 months after infection in asymptomatic persons and patients with pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2.
We studied 7 persons infected with SARS-CoV-2 who were isolated in a community treatment center operated by Seoul National University (SNU) Hospital in Daegu, South Korea (3). Comprehensive monitoring confirmed that these 7 patients were asymptomatic (4). We also evaluated 11 SARS-CoV-2–positive patients with pneumonia at the Biocontainment Unit in the SNU Hospital and SNU Bundang Hospital. We classified each case of pneumonia as subtle (i.e., infiltrations observed only on computed tomography) or apparent (i.e., infiltrations observed on plain chest radiograph) (Appendix). All patients provided informed consent.
We evaluated the antibody responses at 2 and 5 months after infection, as reported (1). We semiquantitatively measured IgG against SARS-CoV-2 using ELISA (Euroimmun, ) with the recombinant S1 domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein as the antigen. We interpreted the optical density ratio (sample/calibrator) as negative (<0.8), borderline (>0.8 to <1.1), or positive (>1.1), according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. We also conducted neutralization assays as previously described (5) using BetaCoV/Korea/SNU01/2020 virus (6) and 2-fold serially diluted plasma samples (2–4,096-fold). We recorded the highest dilution of plasma that showed inhibition activity of SARS-CoV-2 as the neutralizing antibody titer. We considered a >4-fold reduction in antibody titer to be a waning response. The Institutional Review Boards of Seoul National University Hospital approved the study (IRB no. H-2004-158-1118).
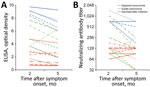
Two months after infection, 11 (100%) patients with pneumonia and 5 (71%) with asymptomatic infection had positive ELISA results. Five months after infection, 5 (100.0%) patients with apparent pneumonia, 5 (83.3%) with subtle pneumonia, and 4 (57.1%) with asymptomatic infection had positive ELISA results. The mean ELISA optical density decreased significantly from 2 to 5 months after infection (4.93 at 2 months vs. 4.09 at 5 months; p = 0.01).
Two months after infection, all patients had neutralizing antibodies. Antibody titers correlated with disease severity; the geometric mean titer was 105 among symptomatic persons, 161 among patients with subtle pneumonia, and 891 among patients with apparent pneumonia. Five months after infection, all patients still had neutralizing antibodies, but the geometric mean titer decreased significantly (219.4 at 2 months vs. 143.7 at 5 months; p = 0.03). In the linear regression model, the decline was significantly associated with the antibody levels at 2 months as measured by ELISA (r = 0.536, p = 0.02) and the neutralization assay (r = 0.563, p = 0.02) (Appendix Figure). The waning neutralizing antibody response occurred in 2 (40%) of 5 patients with apparent pneumonia and 2 (33%) of 6 with subtle pneumonia, but none of the asymptomatic persons (Figure).
Determining the longevity of humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 is essential to predicting herd immunity to coronavirus disease. Among patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, which is closely related to SARS-CoV-2, a total of 90% maintained IgG for 2 years and 50% for 3 years (7). However, humoral immunity to common human coronavirus is short-lived; antibodies against seasonal coronaviruses return to baseline levels by 52 weeks after infection, enabling homologous reinfections (8). A recent study showed that the antibody titers of patients with mild coronavirus disease declined more quickly than did those of patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (9).
Our findings demonstrate waning humoral immunity in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. We documented the decline of neutralizing antibody titers in asymptomatic and symptomatic patients. In this study, the initial neutralizing antibody reaction appeared to correlate with the severity of the disease. However, patients with pneumonia were considerably older than asymptomatic persons, and increasing age is associated with a stronger neutralizing antibody response (10). In this study, neutralizing antibody titer decreased more in symptomatic than asymptomatic patients. Our study reinforces the concern that naturally acquired humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 might not be long-lasting.
Dr. Choe is a clinical scientist at Seoul National University Hospital. His research interests focus on preventing healthcare-associated infection and responding to emerging infectious diseases.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kyung Sook Ahn for administrative support. We thank Areum Jo and Su Jin Choi for technical support.
This project was supported by the research fund of Seoul National University Hospital (grant no. 04-2020-0030). The funding agencies had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
References
- Choe PG, Kang CK, Suh HJ, Jung J, Kang E, Lee SY, et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 at 8 weeks postinfection in asymptomatic patients. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:2484–7.
- Long QX, Tang XJ, Shi QL, Li Q, Deng HJ, Yuan J, et al. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat Med. 2020;26:1200–4.
- Kang E, Lee SY, Jung H, Kim MS, Cho B, Kim YS. Operating protocols of a community treatment center for isolation of patients with coronavirus disease, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:2329–37.
- Choe PG, Kang EK, Lee SY, Oh B, Im D, Lee HY, et al. Selecting coronavirus disease 2019 patients with negligible risk of progression: early experience from non-hospital isolation facility in Korea. Korean J Intern Med (Korean Assoc Intern Med). 2020;35:765–70.
- Shen C, Wang Z, Zhao F, Yang Y, Li J, Yuan J, et al. Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma. JAMA. 2020;323:1582–9.
- Park WB, Kwon NJ, Choi SJ, Kang CK, Choe PG, Kim JY, et al. Virus isolation from the first patient with SARS-CoV-2 in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35:
e84 . - Wu LP, Wang NC, Chang YH, Tian XY, Na DY, Zhang LY, et al. Duration of antibody responses after severe acute respiratory syndrome. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1562–4.
- Callow KA, Parry HF, Sergeant M, Tyrrell DA. The time course of the immune response to experimental coronavirus infection of man. Epidemiol Infect. 1990;105:435–46.
- Ibarrondo FJ, Fulcher JA, Goodman-Meza D, Elliott J, Hofmann C, Hausner MA, et al. Rapid decay of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in persons with mild Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1085–7.
- Wang X, Guo X, Xin Q, Pan Y, Hu Y, Li J, et al. Neutralizing antibodies responses to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 inpatients and convalescent patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;
ciaa721 .
Figure
Suggested citation for this article: Choe PG, Kang CK, Suh HJ, Jung J, Song K-H, Bang JH, et al. Waning antibody responses in asymptomatic and symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Jan [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2701.203515
1These first authors equally contributed to this article.





















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario