
Joint Chiefs say mind, body, spirit all part of Total Force Fitness
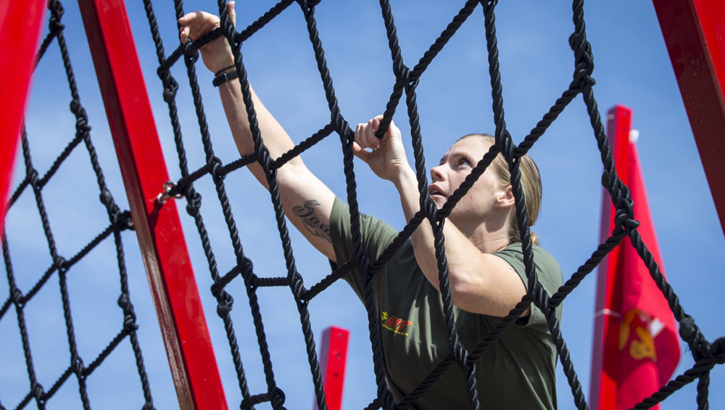

A Marine competes in the High Intensity Tactical Training Championship at Marine Corps Base Quantico, Virginia. Total Force Fitness offers a framework for improving wellness and resilience of military members and their families. The eight TFF domains are medical and dental preventive care, environmental, nutritional, psychological, social, physical, financial, and ideological and spiritual. (U.S. Marine Corps photo by James Frank)
Fitness of mind, body, and spirit is inherently connected with military service. But the understanding of this relationship is constantly evolving as our operational and family commitments change. For 2020, the Military Health System is focusing on Total Force Fitness, a comprehensive framework for improving readiness and resilience of the nation’s military, families, and the communities that support them.
The concept of Total Force Fitness is not new. As early as 2006, the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USUHS) was investigating the aspects that led to human optimal performance or HPO, allowing service members to excel in an operational environment. In 2009, then-Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, Adm. Michael Mullen, commissioned USUHS to develop the Total Force Fitness concept into a CJCS Directive that would address the intersection of health, fitness, and performance optimization.
"[Adm.] Mullen recognized that it required Total Force Fitness to defend our nation,” said USPHS Capt. (Dr.) Kimberly Elenberg, chief, Total Force Fitness branch, Public Health Division, Defense Health Agency.
Mullen realized that “Total force fitness is more than a physical fitness,” he wrote in the August 2010 supplement to Military Medicine, Volume 175, No. 8. “It is the sum total of the many facets of individuals, their families, and the organizations to which they serve. It is not something that someone achieves twice a year for a test. It is a state of being.”
USUHS staff discovered that much of the research on human performance centered on “prevention of disease through physical examinations, vaccinations, health risk screening, enhanced exercise, and the reduction of unhealthy habits, such as smoking and alcohol use.” But with the constant demands placed on service members and their families, more emphasis needed to focus on what factors contributed to resiliency.”
Mullen, with the help of experts at USUHS and the services, developed Total Force Fitness into a concept, adaptable by the services, that included more than the physical aspects of health. They wanted a program that would lead to a military force that could adapt to changing requirements and be resilient to stress. Later this year, a new CJCS Directive will update the Total Force Fitness concept, outlining eight dimensions that help the services achieve total force fitness.
The dimensions were derived from a variety of sources, including current practices on medical fitness, psychological resilience, physical fitness and injury screening, and integrated health approaches. The Total Force Fitness concept integrates health, resilience, and human performance into the following domains:
- Physical Fitness: the ability to physically accomplish all aspects of human performance while remaining mission capable and avoiding injury.
- Environmental Fitness: the ability to optimally perform in any environment, including worldwide, garrison, training, and operational environments.
- Medical and Dental Fitness: the ability to sustain health and wellness and facilitate restoration to meet established medical and dental standards for fitness for duty, return to duty, and medical readiness.
- Nutritional Fitness: the ability to sustain an optimal level of performance through consuming foods, supplements, and beverages in adequate quantities, quality (nutrient content), and proportions.
- Spiritual Fitness: the ability to operationalize one’s spirituality to optimize performance. Spirituality is composed of beliefs and practices that strengthen connectedness with sources of hope, meaning, and purpose.
- Psychological Fitness: the ability to integrate and improve cognitive, emotional, and behavioral capacities to optimize performance and ensure mission readiness.
- Social Fitness: the ability to engage in productive personal and professional relationships, positively interact with unit and command networks, and leverage resources that promote overall well-being and optimal performance.
- Financial Fitness: the combination of attitude, knowledge, skills, and self-efficacy needed to make and exercise money management decisions that best support the circumstances of the service member’s life.
DHA’s Total Force Fitness branch, working with USUHS and the Consortium for Health and Military Performance (CHAMP), will help educate service members and their families to Total Force Fitness concepts. "We'll focus on optimizing the [military] communities’ ability to better understand, assess, and maintain mind, body, and spirit, to include psychological and cognitive wellness," Elenberg said.
The CHAMP website and Health.mil will provide updates and resources throughout the year that military health practitioners, service members, and their families can use to learn more about how they can achieve and support Total Force Fitness.
HPV vaccine now recommended for those up to age 45
Article
1/14/2020
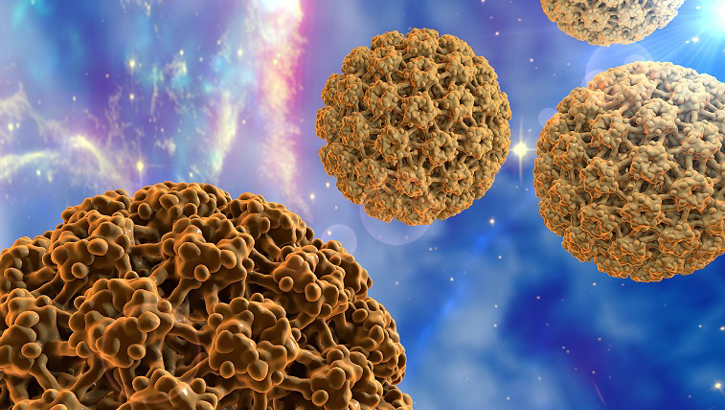
HPV shot protects against a host of diseases in men, women
U.S. Transportation Command: DoD’s manager for global patient movement
Article
1/9/2020
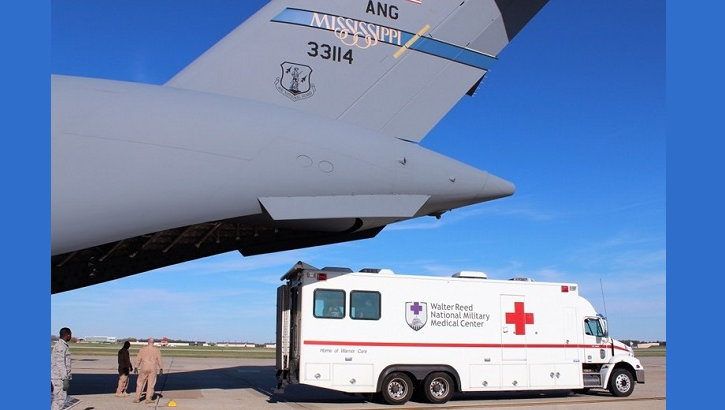

On a weekly basis, USTRANSCOM moves up to 40 patients from overseas to CONUS
Navy Medicine demonstrates Virtual Health options to Africa
Article
1/6/2020
Djibouti hosts the largest U.S. American military base on the African continent
Air Force studies fatigue, sleep to enhance readiness
Article
12/31/2019
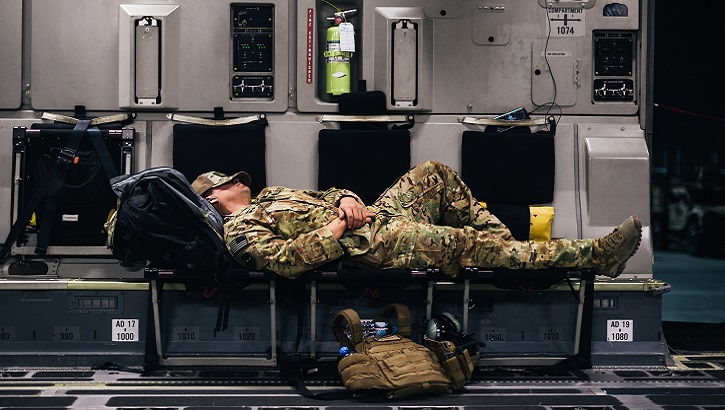

Good sleep habits are closely related to overall health and performance
Guard and Reserve crucial to CCATT expansion
Article
12/20/2019
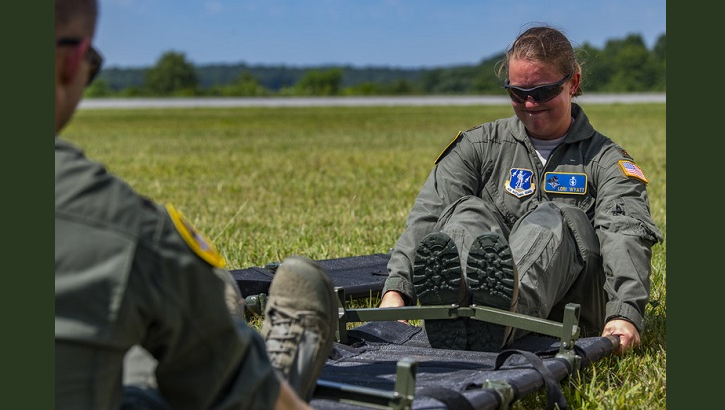

The Guard and Reserve support the bulk of aeromedical evacuation, CCATT capabilities
Air Force, Army medics save groom
Article
12/19/2019
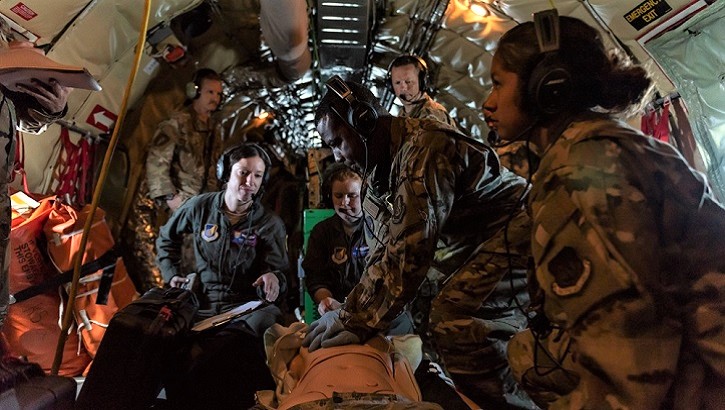
NCO’s first aeromedical evacuation mission was definitely challenging
McCaffery AMSUS Remarks 2019
Publication
12/5/2019
McCaffery statements made during the 2019 annual meeting of AMSUS
McCaffery calls for military medical strategic framework for warfighting readiness
Article
12/5/2019

'New reality' includes tight synchronization, expanding partnerships
MSMR Vol. 26 No. 12 - December 2019
Report
12/1/2019
A monthly publication of the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch. This issue of the peer-reviewed journal contains the following articles: Editorial: Mitigating the risk of disease from tick-borne encephalitis in U.S. military populations; Tick-borne encephalitis surveillance in U.S. military service members and beneficiaries, 2006–2018; Case report: Tick-borne encephalitis virus infection in beneficiaries of the U.S. military healthcare system in southern Germany; Update: Cold weather injuries, active and reserve components, U.S. Armed Forces, July 2014–June 2019
Military medical reform is an opportunity to make trauma care better
Article
11/21/2019

There is an opportunity to bring real change to how the military handles combat trauma care
Preventing seasonal influenza
Article
11/13/2019
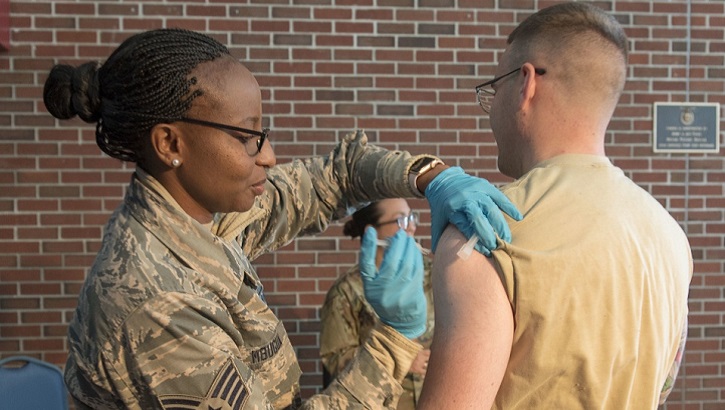
The best way to prevent the flu is to get vaccinated every year
The art of moulage
Article
11/6/2019
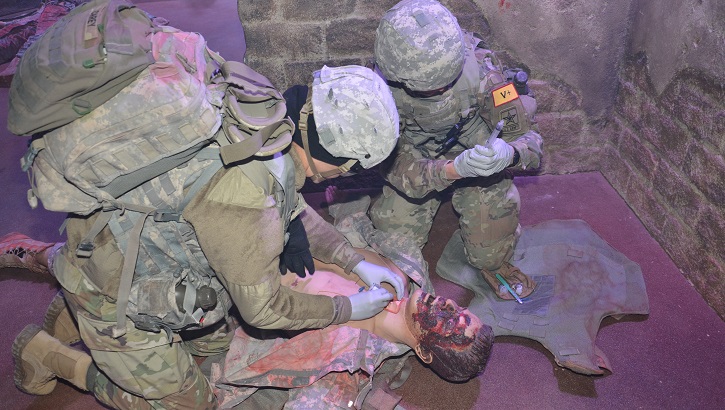

METC combat medic manikins rock realistic wounds
MSMR Vol. 26 No. 11 - November 2019
Report
11/1/2019
A monthly publication of the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch. This issue of the peer-reviewed journal contains the following articles: Editorial: Mitigating the risk of disease from tick-borne encephalitis in U.S. military populations; Tick-borne encephalitis surveillance in U.S. military service members and beneficiaries, 2006–2018; Case report: Tick-borne encephalitis virus infection in beneficiaries of the U.S. military healthcare system in southern Germany; Update: Cold weather injuries, active and reserve components, U.S. Armed Forces, July 2014–June 2019
The Defense Health Agency participates in AUSA 2019 annual meeting
Article
10/18/2019

Focus on quality care, innovation at home and on the battlefield
Holiday Food Safety Tip: Keep Cold Food Cold
Infographic
10/16/2019

Don't let your cold dishes sit out on a counter for more than 2 hours. Keep it chilled at 40 degrees or less.


































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario