
Volume 23, Number 5—May 2017
Etymologia
Etymologia: Fluoroquinolone
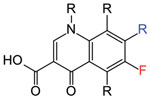
Figure. By Reubot, Public domain, Wikimedia Commons, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=14746558
The first quinolone (quinol[ine] + -one [compound related to ketone]), nalidixic acid (Figure), was isolated as a byproduct of chloroquine (see “quinine”) synthesis and was introduced in 1962 to treat urinary tract infections. In 1980, researchers at the Kyorin Pharmaceutical Company showed that the addition of a fluorine atom to the quinolone ring resulted in an antibiotic with broader antimicrobial activity, which was named norfloxacin, the first fluoroquinolone. In 1983, Bayer published data that showed adding a single carbon atom to norfloxacin—what would become ciprofloxacin—further increased activity. Fluoroquinolones are today among the most frequently used antimicrobial drugs to treat infections in humans and animals.
References
- Dorland’s Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
- Ito A, Hirai K, Inoue M, Koga H, Suzue S, Irikura T, et al. In vitro antibacterial activity of AM-715, a new nalidixic acid analog. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980;17:103–8. DOIPubMed
- Petri WA Jr. Sulfonamides, trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole, quinolones, and agents for urinary tract infections. In: Brunton LL, editor. Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 12th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2011. p. 1463–76.
- Wise R, Andrews JM, Edwards LJ. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983;23:559–64. DOIPubMed






















.png)











No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario