A new DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT is now available.

TAUVID is a drug for the visual detection of aggregated neurofibrillary tangles or NFTs in the brain of adult patients with suspected Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
NFTs are deposits of tau protein that are present in the brains of patients with AD. Alzheimer’s disease is a common degenerative disease of the brain that starts with mild thinking, judging and memory problems and progresses to dementia and death.
TAUVID is injected into a vein by a healthcare provider in preparation for an imaging test (called positron emission tomography scan or PET scan) to detect the NFTs.
See more Drug Trials Snapshots or contact us with questions at Snapshots@fda.hhs.gov.
Drug Trial Snapshot: TAUVID
TAUVID (flortaucipir F 18)
(TAAOW-vihd)
Eli Lilly and Company
Approval date: May 28, 2020
(TAAOW-vihd)
Eli Lilly and Company
Approval date: May 28, 2020
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
TAUVID is a drug for the visual detection of aggregated neurofibrillary tangles or NFTs in the brain of adult patients with suspected Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
NFTs are deposits of tau protein that are present in the brains of patients with AD. Alzheimer’s disease is a common degenerative disease of the brain that starts with mild thinking, judging and memory problems and progresses to dementia and death.
How is this drug used?
TAUVID is injected into a vein by a healthcare provider in preparation for an imaging test (called positron emission tomography scan or PET scan) to detect the NFTs.
What are the benefits of this drug?
TAUVID detects NFTs on PET scan images of the brain.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: TAUVID worked similarly in men and women.
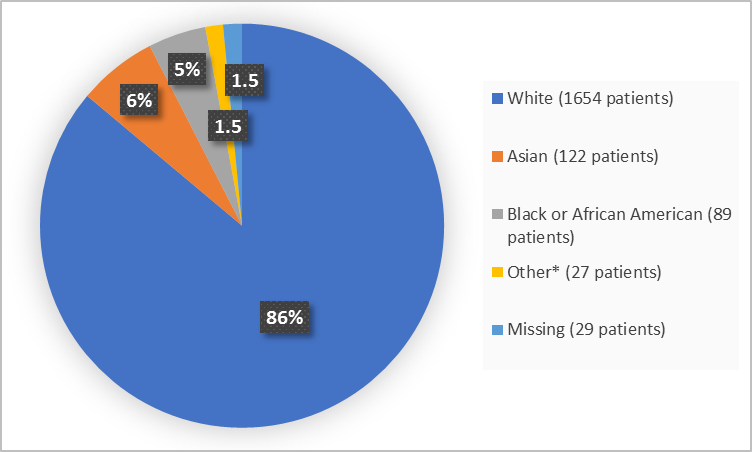
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races were limited; therefore, differences in how TAUVID worked among races could not be determined.
- Age: TAUVID worked similarly in younger and older patients.
What are the possible side effects?
TAUVID is a radioactive drug which may increase the risk of lifetime radiation exposure.
The most common side effects are headache, injection site pain, and increased blood pressure.
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. The number of patients in other races were limited; therefore, differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar in patients younger and those older than 65 years of age.
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved TAUVID based on evidence of 1921 patients from 19 trials conducted at 322 sites in the United States, Australia, Belgium, Canada, France, Japan, Netherlands and Poland.
The figures below summarize how many patients received at least one dose of TAUVID in the clinical trials. These patients provided data for evaluation of TAUVID side effects (safety population). Some of these patients provided data for the benefit of TAUVID (efficacy population) and their demographics are presented in Tables 7 and 8 under MORE INFO #5.
Figure 1. Demographics by Sex (safety population)
FDA Review
Figure 2. Demographics by Race (safety population)
*Includes American Indian or Alaska Native, Multiple, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander and Other
FDA Review
FDA Review
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age group in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Demographics by Age (safety population)
FDA Review
Figure 4. Demographics by Ethnicity (safety population)
* as per local regulatory authority
FDA Review
FDA Review
How were the trials designed?
The benefit of TAUVID was evaluated in two clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT02516046 and Trial 2/NCT03901092). All patients received a single intravenous dose of TAUVID before getting a PET scan to detect NFTs.
In Trial 1, PET scan images of terminally ill patients were read as positive or negative for NFTs by five readers who had no knowledge about patient’s condition and compared with brain autopsy findings of NFTs after patients’ death.
In Trial 2, all the images from Trial 1 and additional images from different patients with suspected AD (but not terminally ill) were read by five new readers. The trial analyzed how similar the readings were among different readers, and between the readings of terminally ill patients and patients with suspected AD.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
























.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario