
A new DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT is now available.
Drug Trials Snapshots: VYLEESI
VYLEESI is a drug for the treatment of women with acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) who have not gone through menopause.
VYLEESI is administered at least 45 minutes before sexual activity using an autoinjector (medical device that delivers a dose of the drug). The autoinjector delivers the dose as an injection under the skin (subcutaneous) of the abdomen or thigh
See more Drug Trials Snapshots or contact us with questions at Snapshots@fda.hhs.gov
VYLEESI (bremelanotide injection)
vahy-lee-see
AMAG Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Approval date: June 21, 2019
vahy-lee-see
AMAG Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Approval date: June 21, 2019
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
VYLEESI is a drug for the treatment of women with acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) who have not gone through menopause.
HSDD is acquired and generalized if the woman has not had problems with low sexual desire in the past, and if she has symptoms no matter the type of sexual activity, the situation, or the sexual partner.
Women with HSDD have low sexual desire that is troubling to them. Their low sexual desire is not due to:
- a medical or mental health problem,
- problems in the relationship, or
- a medicine or other drug use.
How is this drug used?
VYLEESI is administered at least 45 minutes before sexual activity using an autoinjector (medical device that delivers a dose of the drug). The autoinjector delivers the dose as an injection under the skin (subcutaneous) of the abdomen or thigh.
Patients should only take one dose of VYLEESI within 24 hours and should not take more than 8 doses a month.
What are the benefits of this drug?
In clinical trials, VYLEESI improved sexual desire and decreased the level of feeling bothered by low sexual desire in comparison to placebo.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: All patients in the trials were women.
- Race: The majority of patients in the trials were White. The number of patients in other races was limited. Therefore, differences in how well VYLEESI worked among other races could not be determined.
- Age: VYLEESI worked similarly in tested age groups.
What are the possible side effects?
VYLESSI may cause important side effects including:
- temporary increase in blood pressure and decrease in heart rate after each dose,
- darkening of the gums and of the skin on the face and breasts, and
- nausea, which can be severe and require medical treatment.
Most common side effects of VYLESSI are nausea, flushing, injection site reactions, headache and vomiting.
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: All patients in the trial were women.
- Race: The occurrence of side effects was similar among White and Black or African American patients except for darkening of the skin which occurred more frequently in Black or African American patients. The number of patients in other races was limited. Therefore, differences in the occurrence of side effects among other races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar among tested age groups.
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved VYLEESI based on evidence from two clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT02333071 and Trial 2/NCT02338960) of 1267 women 19-56 years of age with acquired, generalized HSDD. The trials were conducted in Canada and the United States.
Figure 1 summarizes how many women were in the clinical trials used to evaluate safety.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (safety population)
FDA Review
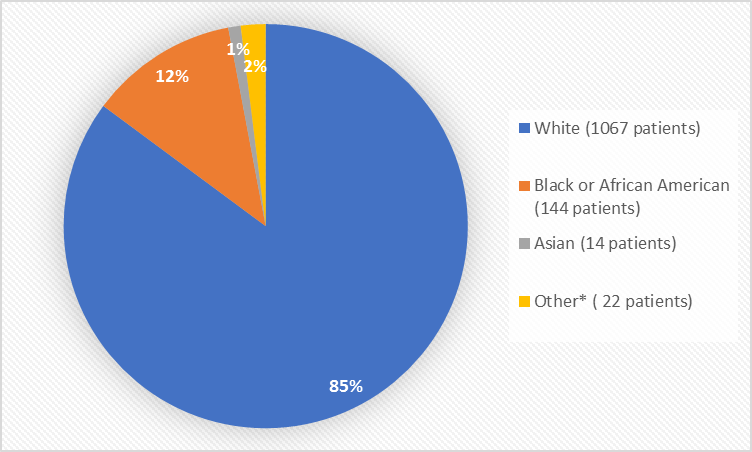
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by race in the clinical trials used to evaluate safety.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race (safety population)
*Other includes American Indian
Table 1. Demographics of Trials by Race (safety population)
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage of Patients |
|---|---|---|
| White | 1067 | 85% |
| Black or African American | 144 | 12% |
| Asian | 14 | 1% |
| American Indian | 7 | Less than 1% |
| Other and multiple | 15 | 1% |
FDA Review
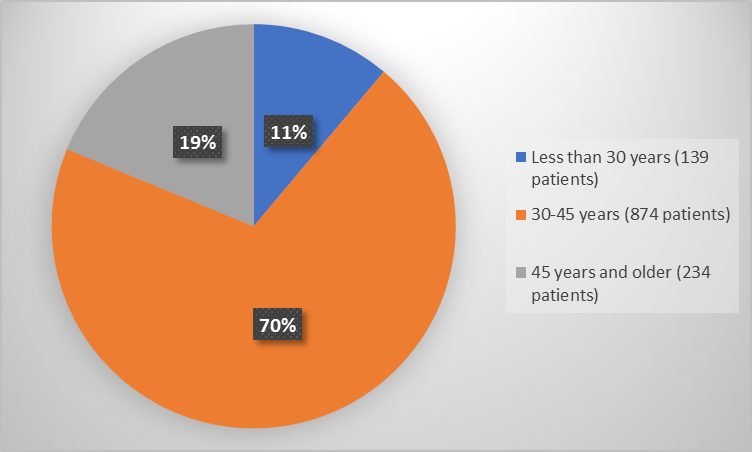
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
How were the trials designed?
The benefits and side effects of VYLEESI were evaluated in two trials of women 19 to 56 years old who had not reached menopause and who had acquired, generalized HSDD for at least 6 months. Patients used an autoinjector to inject VYLEESI or placebo under the skin of the thigh or abdomen 45 minutes before sexual activity, when needed, over a 24-week period. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given during the trials.
The trials measured the change from when treatment was started to when treatment was stopped in the level of sexual desire and the level of feeling bothered by low sexual desire. The sexual desire score rates the level of sexual desire using a scale where higher scores indicate more desire. The score for feeling bothered by low sexual desire was measured by one item in the Female Sexual Distress Scale where lower scores indicate less bother.
After completing the 24-week treatment period, patients in both the VYLEESI group and placebo group had the option to use VYLEESI for an additional year.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.






















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario