
Scientists develop accurate, wearable voice recognition device
A team of scientists has developed a flexible and wearable voice sensor that accurately recognizes the user’s voice, without being affected by surrounding voices.
The study, which was published in the journal, Nature Communications, shows how the team developed a flexible and wearable sensor that can precisely recognize voice through vibrations of the skin in the neck area.
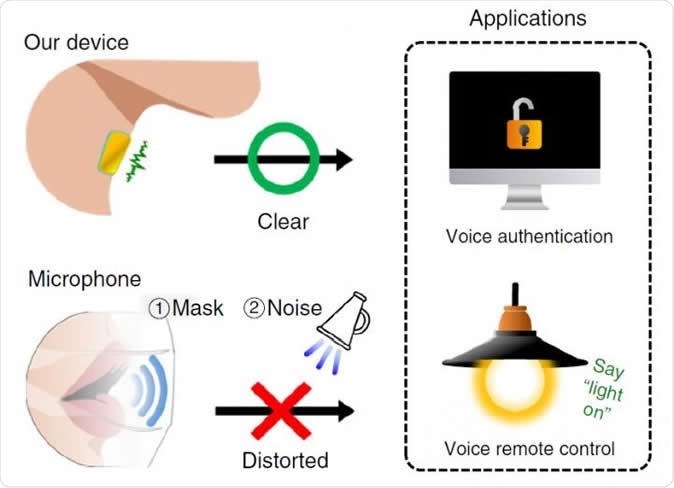
Schematic image of the comparison between our device and a reference microphone (Bruel & Kjaer, microphone type 4192, sensitivity of 1 V Pa?1) for voice authentication and voice-controlled applications. Image Credit: POSTECH
Accurate voice recognition feature
Today, mobile phones have a voice-recognition feature. People use this feature for a wide range of applications. But, it often bugs down, or it doesn’t work properly due to the presence of surrounding noise. Mobile phones use a microphone that can detect sound pressure for voice recognition.
The researchers from (Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) have successfully devised the vibration responsive sensor, which is attached to the neck without being affected by ambient or surrounding noise, no matter the intensity.
“Here, we present an ultrathin, conformable, and vibration-responsive electronic skin that detects skin acceleration, which is highly and linearly correlated with voice pressure,” the researchers said in the study.
“Here, we present an ultrathin, conformable, and vibration-responsive electronic skin that detects skin acceleration, which is highly and linearly correlated with voice pressure,” the researchers said in the study.
In the past, microphones have been developed to accurately recognize or detect voice across many electronic devices. But, since these microphones on mobile phones aren’t perfect and have many issues, the researchers decided to create one that can’t be influenced by outside noise or surrounding noise.
“Our device is suitable for several promising voice-recognition applications, such as security authentication, remote control systems, and vocal healthcare,” the researchers added.
Neck skin vibration
The sensor, when attached to the neck, can recognize voice through the neck skin vibration. It can’t be influenced by ambient sound or noise, and even the sound’s volume. Air vibration enables the sensor to recognize the voice. Also, the sensitivity lowers because of mechanical resonance and damping effect. Hence, they can’t measure voices quantitatively.
Skin-attachable sensors detect and recognize human voice by examining neck skin vibrations. These vibrations can be measured with several parameters, including velocity, displacement, and acceleration.
In the study, which was supported by the Global Frontier Research Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT in Korea – Center for Advanced Soft Electronics, the researchers were able to demonstrate that the voice pressure is relative to the speeding up of neck skin vibration at several sound pressure levels, ranging from 40 to 7 dBSPL. Thus, the researchers developed a vibration sensory using skin vibration acceleration.
Application of voice recognition sensors
The team successfully showed that the voice recognition sensor can detect voice accurately without vibrational distortion even in a loud and noisy environment.
The results of the study can pave the way to develop voice-recognition inventions further. It can be in the form of a wearable vocal healthcare monitoring device, human-machine interface, and electronic skin.
"This research is very meaningful in a way that it developed a new voice-recognition system which can quantitively sense and analyze voice and is not affected by the surroundings,” Kilwon Cho, Chemical Engineering and Professor Yoonyoung Chung of Electronic and Electric Engineering from POSTECH, said in a statement.
“It took a step forward from the conventional voice-recognition system that could only recognize voice qualitatively,” he added.
Voice recognition
Voice recognition is a computer program or software that can decode the human voice. It’s the ability of an electronic device to recognize a person’s voice that is unique, like a fingerprint. Speech recognition, on the other hand, is the ability of the software to recognize spoken words, not the voice characteristics of the user.
Today, there are many applications of voice recognition. For one, people use voice recognition as a security pass for their electronic devices, while others use voice recognition in software programs such as Google Voice, digital assistant programs, car Bluetooth systems, automated phone systems, voice technology in finance, and public transportation, among others.
In the future, voice recognition and the artificial intelligence behind it will undergo innovations that can lead to breakthroughs. Companies and scientists are experimenting with integrating their products, services, and studies with digital voice-assistants.
Journal reference:
Lee, S., Kim, J., Yun, I., Bae, G., Kim, D., Park, S., Yi, I., Moon, W., Chung Y., and Cho, K. (2019). An ultrathin conformable vibration-responsive electronic skin for quantitative vocal recognition. Nature Communications. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-10465-w






















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario