
A new DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT is now available
POLIVY is a drug used with other drugs to treat adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) whose disease has come back or has not improved after at least two previous treatments. DLBCL is a fast-growing cancer of the lymph system, which is part of the body’s immune system.
POLIVY is given by a healthcare provider directly into the bloodstream through a needle in the vein, also known as intravenous or IV infusion.
See more Drug Trials Snapshots or contact us with questions at Snapshots@fda.hhs.gov.
Drug Trials Snapshots: POLIVY
POLIVY (polatuzumab vedotin-piiq)
poe li' vee
Genentech, Inc.
Approval date: June 10, 2019
poe li' vee
Genentech, Inc.
Approval date: June 10, 2019
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
POLIVY is used with other drugs to treat adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) whose disease has come back or has not improved after at least two previous treatments.
DLBCL is a fast-growing cancer of the lymph system, which is part of the body’s immune system.
How is this drug used?
POLIVY is given by a healthcare provider directly into the bloodstream through a needle in the vein. This is known as an intravenous, or IV infusion. POLIVY is given every 21 days for 6 cycles together with bendamustine (a type of chemotherapy) and a rituximab product (a combination known as “BR”).
What are the benefits of this drug?
In a clinical trial, of 40 patients with DLBCL assigned to get POLIVY plus BR, 63% had complete or partial shrinkage of their tumors (remission), and 40% had complete shrinkage (complete remission) after finishing treatment.
In comparison, of 40 patients assigned to get BR alone, 25% had a remission, and 18% had a complete remission after finishing treatment.
POLIVY was approved under FDA’s accelerated approval program, which provides earlier patient access to a promising new drug while the company continues to conduct clinical trials to confirm that the drug works well.
There are ongoing clinical trials to confirm the clinical benefit of POLIVY.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
The trial that looked at the benefit of POLIVY was too small to determine if there were any differences in sex, race and age subgroups.
What are the possible side effects?
POLIVY may cause serious side effects including nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy), infusion related allergic reactions, bone marrow suppression, infections including a rare type of brain infection (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy), tumor lysis syndrome (caused by fast breakdown of cancer cells), liver damage, and harm to an unborn baby.
The most common side effects of POLIVY are low blood cell counts, nerve damage, fatigue, diarrhea, fever, decrease appetite, and pneumonia.
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
The trial that looked at the side effects of POLIVY was too small to determine if there were any differences in sex, race and age subgroups.
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved POLIVY based primarily on evidence from one clinical trial (NCT02257567) that was conducted in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Asia. Patients who participated in the trial had lymphoma that came back or did not improve after prior treatment.
Presented below is the trial population that provided data to assess the benefit of POLIVY (called the efficacy population).
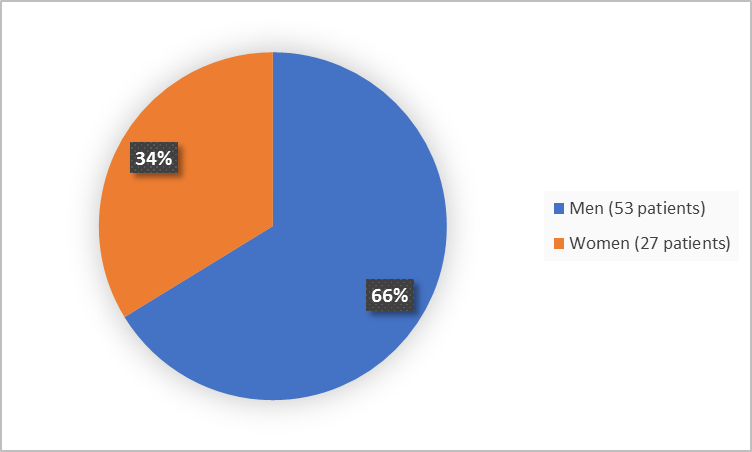
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women participated in the trial (efficacy population).
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (Efficacy Population)
FDA Review
Figure 2 and Table 1 below summarize patients by race in the trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race (Efficacy Population)
FDA Review
Table 1. Baseline Demographics by Race (Efficacy Population)
Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
White | 57 | 71 |
Black or African American | 3 | 4 |
Asian | 10 | 13 |
American Indian or Alaska Native | 1 | 1 |
Unknown | 9 | 11 |
FDA review
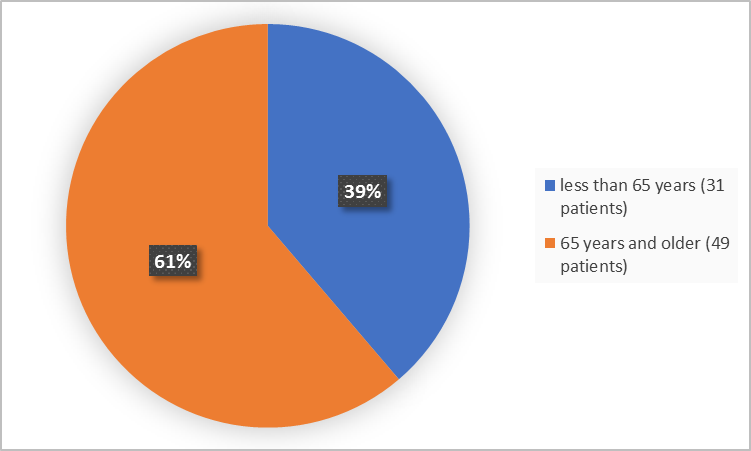
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age (Efficacy Population)
FDA Review
How were the trials designed?
There was one trial that evaluated the benefit and side effects of POLIVY in patients with lymphoma whose disease has returned or has not improved after previous treatment.
Patients received either POLIVY in combination with bendamustine and rituximab or bendamustine and rituximab only every 21 days for 6 treatment cycles. Both patients and health care providers knew which treatment had been given.
The benefit of POLIVY was evaluated by measuring how many patients treated with POLIVY in combination with bendamustine and rituximab had a remission (complete or partial tumor shrinkage) in comparison to patients treated with bendamustine and rituximab only, and how long that response lasted.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.






















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario