
2019 Maps Show Increases in Adult Obesity Prevalence, Persistent Disparities
Twelve states now have an adult obesity prevalence at or above 35 percent, according to new CDC adult obesity prevalence maps. The 12 states are Alabama, Arkansas, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Mississippi, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, and West Virginia. This is up from 9 states in 2018 and 6 states in 2017. The 2019 maps show self-reported adult obesity prevalence by race, ethnicity, and location for 49 states, the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico. Data are not available for New Jersey. The maps use combined 2017-2019 data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS). Adult obesity prevalence ranged from 23.8 percent in Colorado and the District of Columbia to 40.8 percent in Mississippi. Obesity is a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or above. |
|---|
Prevalence of Self-Reported Obesity Among US Adults by State and Territory, BRFSS, 2019

The 2019 maps show notable racial and ethnic disparities:
|
|---|
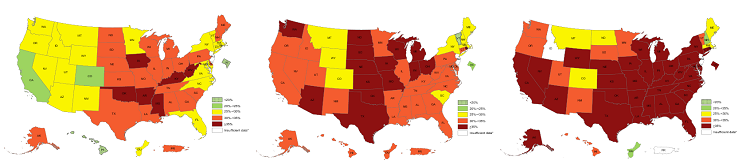
Prevalence of Self-Reported Obesity Among, From Left, Non-Hispanic White Adults, Hispanic Adults, and Non-Hispanic Black Adults by State and Territory, BRFSS, 2017-2019 |
|---|
People who have obesity, compared to those with a healthy weight, are at increased risk for many other serious diseases and health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, stroke, and many types of cancer. In addition, obesity costs the US healthcare system $147 billion a year.
Obesity also worsens outcomes from COVID-19, increasing the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Highlights of a CDC summary statement on obesity and race and ethnicity as related to COVID-19 risk include:
- Disparities in obesity prevalence underscore the need to remove barriers to health and ensure that communities support a healthy, active lifestyle for all.
- While system and environment changes can take time, everyone can take small steps now to maintain or improve their health and protect themselves during this pandemic.
- Being active and eating a healthy diet can support optimal immune function and help prevent or manage chronic diseases that worsen outcomes from COVID-19.
- These actions, as well as getting enough sleep and finding healthy ways to cope with stress, can help with weight maintenance and improve overall health.
Factors contributing to obesity include neighborhood design, access to safe and convenient places for physical activity, and access to healthy, affordable foods and beverages. The racial and ethnic disparities in obesity underscore the need to address social determinants of health such as poverty, education, and housing. CDC works with national, state, and local groups to ensure that obesity prevention and management starts early, and that everyone has access to good nutrition and safe places to be physically active. Turning the tide on obesity will take a comprehensive effort by all parts of society. These maps can help by showing where the burden of obesity is greatest. |
|---|
Notes on Language and Images We encourage use of person-first language, such as adults with obesity, when discussing obesity and other chronic diseases. Also see The Obesity Action Coalition’s guidelines for media portrayals of individuals affected by obesity. |
|---|





















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario