
Cancer and Men
Men have higher rates of getting and dying from cancer than women. You can lower your chance of getting cancer by staying up-to-date on screening tests and making healthy choices.
Cancer Screening Tests
Screening means checking your body for cancer before you have symptoms. All screening tests have benefits and harms. Screening is recommended when the benefits outweigh the harms.
Getting screening tests regularly may prevent colorectal (colon) cancer or find it early. Lung cancer screening is recommended for some people who are at high risk. The goal of screening for prostate cancer is to find cancers that may be at high risk for spreading if not treated, and to find them early before they spread.
Cancer Screening Tests
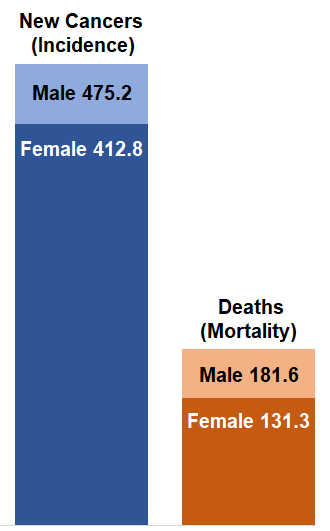
Cancer Rates, All Types of Cancer, United States, 2017
In the United. States in 2017, men had higher rates of getting and dying from cancer than women. Source: U.S. Cancer Statistics.
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancers begin as precancerous polyps (abnormal growths) in the colon or rectum. They may not cause any symptoms, especially early on. Colorectal cancer screening can find precancerous polyps so they can be removed before they turn into cancer. Screening can also find colorectal cancer early, when treatment works best.
Most people should begin screening for colorectal cancer soon after turning 50, then continue getting screened as recommended by your doctor. You may need to be screened earlier or more often than other people if you are at increased risk of getting colorectal cancer.
Several screening tests can be used to find colorectal cancer. Some are done in a doctor’s office, and some can be done at home. Talk to your doctor about which test is right for you.
Lung Cancer
The only recommended screening test for lung cancer is low-dose computed tomography.
Lung cancer screening is done yearly on people who—
- Are between 55 and 80 years old, and
- Smoke now or have quit within the past 15 years, and
- Have a history of heavy smoking (30 pack years or more).
A pack year is smoking an average of one pack of cigarettes per day for one year. For example, a person could have a 30 pack-year history by smoking one pack a day for 30 years or two packs a day for 15 years.
If you are thinking about getting screened, talk to your doctor.
Prostate Cancer
This video helps men understand their prostate cancer screening options.
The goal of screening for prostate cancer is to find cancers that may be at high risk for spreading if not treated, and to find them early before they spread. However, most prostate cancers grow slowly or not at all.
A blood test called a prostate specific antigen (PSA) test is commonly used to screen for prostate cancer.
If you are thinking about being screened, learn about the possible benefits and harms of screening, and talk to your doctor about your personal risk factors.
Healthy Choices
You can do several things to lower the chances that you’ll get cancer. Some of the most important are—
- Staying away from tobacco. If you smoke, try to quit, and stay away from other people’s smoke.
- Limiting the amount of alcohol you drink.
- Protecting your skin from the sun.
- Maintaining a healthy weight, and staying physically active.
Featured Resources
























.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario