A new DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT is now available.

EXEM FOAM is a drug for the detection of fallopian tube patency (openness) in women with known or suspected infertility.
Fallopian tubes are part of female reproductive system and, if blocked, could be a reason for infertility (failure to become pregnant).
EXEM FOAM is infused by a healthcare professional into uterus to allow for visual assessment of fallopian tubes during an ultrasound examination called sonohysterosalpingography.
See more Drug Trials Snapshots or contact us with questions at Snapshots@fda.hhs.gov.
Drug Trials Snapshots: EXEM FOAM
EXEM FOAM (air polymer-Type A) intrauterine foam
Eks em fōm
ExEm Foam Inc.
Approval date: November 7, 2019
Eks em fōm
ExEm Foam Inc.
Approval date: November 7, 2019
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
EXEM FOAM is a drug for the detection of fallopian tube patency (openness) in women with known or suspected infertility.
Fallopian tubes are part of female reproductive system and, if blocked, could be a reason for infertility (failure to become pregnant).
How is this drug used?
EXEM FOAM is infused by a healthcare professional into uterus to allow for visual assessment of fallopian tubes during an ultrasound examination called sonohysterosalpingography.
What are the benefits of this drug?
When compared to the standard procedure, a high proportion of fallopian tubes were correctly identified as either open or as blocked using EXEM FOAM during sonohysterosalpingography.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
Differences among subgroups were not analyzed because all patients were women of similar age and patients’ race was not reported.
What are the possible side effects?
Sonohysterosalpingography with EXEM FOAM may cause serious side effects including harm to unborn baby (if pregnancy was not recognized prior to EXEM FOAM use) and infection of reproductive system.
The most common adverse reactions are pelvic and abdominal pain, nausea and faintness (caused by a nerve and blood vessel reaction called vasovagal reaction) and post-procedure spotting.
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
Differences among subgroups were not analyzed because all patients were women of similar age and patients’ race was not reported.
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved EXEM FOAM based on the literature reports.
To evaluate how well EXEM FOAM works, FDA primarily used data from two trials (Trial A from the article by Riganelli et al. 2018* and Trial B by from the article by Ludwin et al. 2017**). Trial A was conducted at one site in Italy and Trial B at 3 sites in Poland.
Evaluation of side effects was based on multiple literature reports and collected safety reports from countries where EXEM FOAM is already approved.
*Riganelli L., Casorelli A. et al. Ultrasonography reappraisal of tubal patency in assisted reproduction technology patients: comparison between 2D and3D-sonohysterosalpingography. A pilot study. Minerva Ginecologica 2018, l;70(2):123-8
**Ludwin I., Ludwin, A. et al. Accuracy of hysterosalpingo-foam sonography in comparison to hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography with air/saline and to laparoscopy with dye. Human Reproduction 2017,.32-(4):758–769,
**Ludwin I., Ludwin, A. et al. Accuracy of hysterosalpingo-foam sonography in comparison to hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography with air/saline and to laparoscopy with dye. Human Reproduction 2017,.32-(4):758–769,
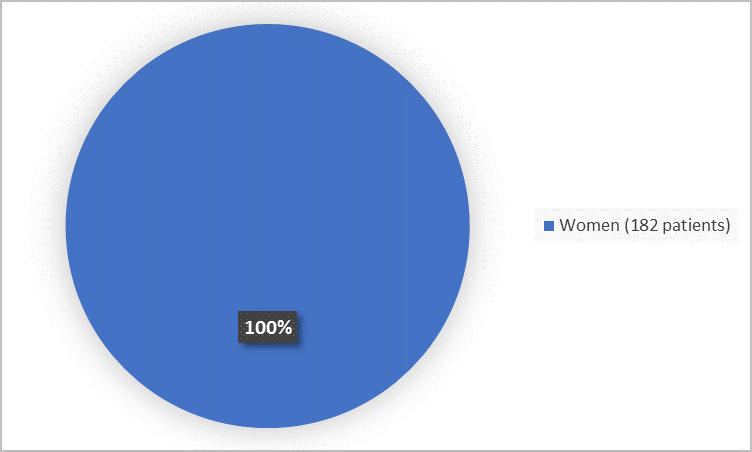
The figure below summarizes how many women participated in combined Trials A and B.
Figure 1. Demographics by Sex
FDA Review
Demographics by Race - not reported
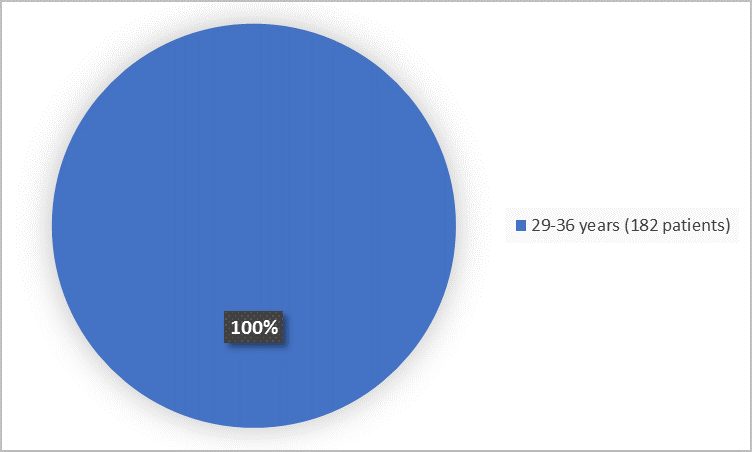
Figure 2 summarizes the percentage of patients by age group.
Figure 2. Demographics by Age
How were the trials designed?
The benefit and side effects of EXEM FOAM were primarily established on the reports of clinical trials from the literature.
The benefit was established using data from two clinical trials in women who had known or suspected infertility. In both trials, patients received EXEM FOAM and underwent ultrasound imaging to see if the fallopian tubes were open or blocked.
The benefit of EXEM FOAM was assessed by comparing the accuracy of EXEM FOAM/ultrasound findings on fallopian tube openness in comparison to the standard procedure.
The side effects of EXEM FOAM were collected from multiple sources including literature reports.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.


































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario