Volume 26, Number 12—December 2020
Dispatch
Differential Tropism of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 in Bat Cells
On This Page
Downloads
Altmetric
Susanna K.P. Lau1 , Antonio C.P. Wong1, Hayes K.H. Luk1, Kenneth S.M. Li, Joshua Fung, Zirong He, Flora K.K. Cheng, Tony T.Y. Chan, Stella Chu, Kam Leng Aw-Yong, Terrence C.K. Lau, Kitty S.C. Fung, and Patrick C.Y. Woo
, Antonio C.P. Wong1, Hayes K.H. Luk1, Kenneth S.M. Li, Joshua Fung, Zirong He, Flora K.K. Cheng, Tony T.Y. Chan, Stella Chu, Kam Leng Aw-Yong, Terrence C.K. Lau, Kitty S.C. Fung, and Patrick C.Y. Woo
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 did not replicate efficiently in 13 bat cell lines, whereas severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replicated efficiently in kidney cells of its ancestral host, the Rhinolophus sinicus bat, suggesting different evolutionary origins. Structural modeling showed that RBD/RsACE2 binding may contribute to the differential cellular tropism.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a global pandemic, affecting 213 countries with >2.7 million confirmed cases and 190,000 fatalities as of April 25, 2020 (1). Its causative agent was identified as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 2 (SARS-CoV2), which belongs to the same coronavirus species as SARS-CoV and SARS-related CoVs (SARSr-CoVs) in horseshoe bats (genus Rhinolophus) (2,3). Given the history among some early case-patients of visiting the Huanan seafood market in Wuhan, China, and its genetic close relatedness to SARSr-CoVs in bats and pangolins (2,4), SARS-CoV-2 was suspected to have emerged from wild animals, particularly bats, similar to SARS-CoV. SARS-CoV was a recombinant virus that originated from horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus sinicus) in China before it infected palm civets and then humans (5).
Studying cellular tropism may provide clues to the host range and possible origin of zoonotic viruses. For example, SARS-CoV could replicate efficiently in kidney cells of its primary origin, R. sinicus, but not in other tested bat cells (6). To elucidate the possible origin of SARS-CoV-2, we tested susceptibilities of bat cell lines developed from different species commonly found in southern China to infection by SARS-CoV-2 in comparison with SARS-CoV. The selected bat species harbored a diverse set of coronaviruses, including SARSr-CoVs and Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronaviruses (MERSr-CoVs), which pose potential health threats to humans (7). We also performed structural modeling of the virus/host receptor-binding interface.
SARS-CoV strain HKU-39849 was isolated in Hong Kong during the SARS epidemic as previously described (8). SARS-CoV-2 strain HK20 was isolated from a patient with COVID-19 in Hong Kong in early February 2020 (3). Thirteen primary or immortalized bat cell lines from 6 different bat species were subjected to infection with SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 at multiplicity of infection of 0.1 as described previously (6,9,10), except with the addition of 2 µg/mL trypsin. The bat species included Miniopterus pusillus, Pipistrellus abramus (harboring Pipistrellus-BatCoV-HKU5), R. sinicus (harboring SARSr-BatCoVs, Rhinolophus-BatCoV-HKU2, Rhinolophus sinicus-BatCoV-HKU32), Tylonycteris pachypus (harboring Tylonycteris-BatCoV-HKU4), Rousettus leschenaultii (harboring many viruses, including Rousettus-BatCoV-HKU9 and Rousettus-BatCoV-HKU10), and Myotis ricketii (harboring Myotis-BatCoV HKU6). Vero cells from African green monkey kidney were used as positive control (Appendix). We determined viral replication efficiency by quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) on cell culture supernatants (Table 1) (6). Cells were considered susceptible to viral infection if qRT-PCR on day 5 postinfection showed >1 log10 increase in viral titer with statistical significance (p<0.05 by Student t-test).
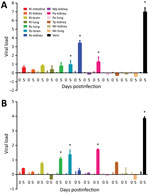
SARS-CoV but not SARS-CoV-2 can replicate efficiently in R. sinicus kidney cells; SARS-CoV showed 3.48 log10-fold increase in viral titer. In contrast, only SARS-CoV-2 can replicate in R. sinicus lung cells, but at a low viral titer (1.08 log10-fold increase). Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 can replicate more efficiently (1.46 log10-fold increase) in R. sinicus brain cells than SARS-CoV (1.09 log10-fold increase), albeit still at low viral titer (Table 2; Figure 1). Both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 can also replicate in P. abramus kidney cells with low viral titers: 1.45 log10-fold increase for SARS-CoV and 1.71 log10-fold increase for SARS-CoV-2. We observed cytopathic effects in SARS-CoV–infected R. sinicus kidney cells and SARS-CoV– or SARS-CoV-2–infected P. abramus kidney cells with rounding of cells (Appendix). We performed immunofluorescence assay on those cell lines with >1 log10-fold increase in viral load (Appendix). M. pusillus kidney cells; R. leschenaultii kidney, brain, intestine, and lung cells; T. pachypus kidney cells; and M. ricketii kidney and lung cells did not support SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-2 infection. Furthermore, both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 replicated less efficiently in Vero cells at 33°C than at 37°C, whereas no difference in viral replication in R. sinicus kidney cells was observed between 33°C and 37°C (Appendix).
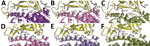
To elucidate whether the receptor-binding interface is a contributing factor for cellular tropism, we modeled the structure of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD) with that of human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2), R. sinicus angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (Rs-ACE2), and P. abramus angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (Pa-ACE2) using homology modeling by SWISS-MODEL () as described previously (11), based on the crystal structure of SARS-CoV-RBD/hACE2. The sequence identity between SARS-CoV RBD (template) and SARS-CoV-2-RBD (template) was >50% and the interface for all RBD/ACE2 was similar (Figure 2). We identified 11 aa differences between SARS-CoV RBD and SARS-CoV-2 RBD sequences that involved 4 of 5 critical residues for hACE2 binding in SARS-CoV RBD. Y442 was one of the 5 critical residues in SARS-CoV RBD. Because F456 is more hydrophobic than Y442 in SARS-CoV-2 RBD, it may disturb the electrostatic interaction with hACE2/Rs-ACE2. The interface for RBD/Pa-ACE 2 was similar to that of RBD/hACE2 (Figure 2), implying that Pa-ACE2 may also serve as the host receptor for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2.
The ability of SARS-CoV but not SARS-CoV-2 to replicate in R. sinicus kidney cells, consistent with previous findings (12), may suggest a different evolutionary origin and path of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV was most closely related to SARSr-Rs-BatCoVs from Yunnan, China, suggesting R. sinicus as its primary origin. It could also use Rs-ACE2 as receptor for cell entry (13), which may explain the efficient replication of SARS-CoV in R. sinicus kidney cells. Although SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to SARSr-CoVs in bats and pangolins, none of the existing animal viruses represents the immediate ancestor of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 was most closely related to SARSr-Ra-BatCoV-RaTG13 (96.1% genome identity) in Rhinolophus affinis from Pu’er, Yunnan (2), except that its RBD region was closest to pangolin-SARSr-CoV-MP789 (86.9% nucleotide identity) in smuggled pangolins from Guangdong, suggesting that SARS-CoV-2 may have evolved through recombination (3). The inability of SARS-CoV-2 to efficiently infect and replicate in R. sinicus cells may imply that R. sinicus bats were unlikely to be its proximal origin. However, bats are the primary origin of SARS-CoV, human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E), and probably MERS-CoV; therefore, SARS-CoV-2 most likely originated from bats. One possibility is that SARS-CoV-2 has restricted bat species tropism. Other bat species, such as R. affinis, may harbor the ancestor of SARS-CoV-2 and can be tested for cellular susceptibilities in future studies. It is also possible that SARS-CoV-2 can no longer replicate in bat cells because of substantial genetic adaptation, such as through natural evolution in an intermediate host before infecting humans.
The difference in critical residues for receptor binding between SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 may have contributed to their differential infectivities in R. sinicus cells, as suggested by results from structural modeling of the receptor-binding interface. Whereas SARS RBD was most closely related to SARSr-Rs-BatCoV-WIV1 from R. sinicus, SARS-CoV-2 RBD was most closely related to the RBD region of pangolin-SARSr-CoV-MP789 from pangolins (14). Mutagenesis studies are needed to investigate whether changes of these amino acid sites may affect binding affinity to the ACE2 of different hosts and restore the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 in R. sinicus cells.
The restricted cellular tropism of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 is different from that of MERS-CoV, which showed broad species tropism in bat cells. MERS-CoV could replicate in >5 bat cell lines (M. ricketti lung, P. abramus kidney, R. sinicus kidney and lung, and R. leschenaultii kidney cells) from 3 bat families (6). Although dromedary camels were the immediate source of MERS-CoV, bats were suggested to be the ultimate evolutionary origin (10,15). Of note, SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and MERS-CoV could all replicate in P. abramus kidneys at low titers. Structural modeling supported that P. abramus ACE2 could serve as host receptor for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. P. abramus is known to harbor Pi-BatCoV-HKU5 from the subgenus Merbecovirus (containing MERS-CoV) but not members of Sarbecovirus (containing SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2) (10,15). P. abramus is a potential accidental host for spillover of and source for emergence of diverse coronaviruses including SARSr-CoVs.
Dr. Lau is a professor and head of the Department of Microbiology at the University of Hong Kong. Her research focuses on microbial genomics for studying emerging infectious diseases including coronaviruses.
Acknowledgments
We thank Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department, Government of Hong Kong, for capture of bats for bat cell development and expert opinion.
This study was partly supported by the theme-based research scheme (project no. T11-707/15-R) of the University Grant Committee; Health and Medical Research Fund of the Food and Health Bureau of HKSAR; Consultancy Service for Enhancing Laboratory Surveillance of Emerging Infectious Disease for the HKSAR Department of Health and the University Development Fund of the University of Hong Kong.
References
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report 96. 2020 Apr 25 [cited 2020 Apr 26].
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579:270–3.
- Lau SKP, Luk HKH, Wong ACP, Li KSM, Zhu L, He Z, et al. Possible bat origin of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:1542–7.
- Lam TT, Jia N, Zhang YW, Shum MH, Jiang JF, Zhu HC, et al. Identifying SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins. Nature. 2020;583:282–5.
- Lau SK, Woo PC, Li KS, Huang Y, Tsoi HW, Wong BH, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:14040–5.
- Lau SKP, Fan RYY, Luk HKH, Zhu L, Fung J, Li KSM, et al. Replication of MERS and SARS coronaviruses in bat cells offers insights to their ancestral origins. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018;7:209.
- Wong ACP, Li X, Lau SKP, Woo PCY. Global epidemiology of bat coronaviruses. Viruses. 2019;11:174.
- Peiris JS, Lai ST, Poon LL, Guan Y, Yam LY, Lim W, et al.; SARS study group. Coronavirus as a possible cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2003;361:1319–25.
- Lau SKP, Wong ACP, Zhang L, Luk HKH, Kwok JSL, Ahmed SS, et al. Novel bat alphacoronaviruses in southern China support Chinese horseshoe bats as an important reservoir for potential novel coronaviruses. Viruses. 2019;11:423.
- Woo PC, Wang M, Lau SK, Xu H, Poon RW, Guo R, et al. Comparative analysis of twelve genomes of three novel group 2c and group 2d coronaviruses reveals unique group and subgroup features. J Virol. 2007;81:1574–85.
- Lau SKP, Zhang L, Luk HKH, Xiong L, Peng X, Li KSM, et al. Receptor usage of a novel bat lineage C betacoronavirus reveals evolution of Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus spike proteins for human dipeptidyl peptidase 4 binding. J Infect Dis. 2018;218:197–207.
- Chu H, Chan JF-W, Yuen TT-T, Shuai H, Yuan S, Wang Y, et al. Comparative tropism, replication kinetics, and cell damage profiling of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV with implications for clinical manifestations, transmissibility, and laboratory studies of COVID-19: an observational study. Lancet Microbe. 2020;1:e14–23.
- Ge XY, Li JL, Yang XL, Chmura AA, Zhu G, Epstein JH, et al. Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor. Nature. 2013;503:535–8.
- Menachery VD, Yount BL Jr, Sims AC, Debbink K, Agnihothram SS, Gralinski LE, et al. SARS-like WIV1-CoV poised for human emergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:3048–53.
- Lau SK, Li KS, Tsang AK, Lam CS, Ahmed S, Chen H, et al. Genetic characterization of Betacoronavirus lineage C viruses in bats reveals marked sequence divergence in the spike protein of pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5 in Japanese pipistrelle: implications for the origin of the novel Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J Virol. 2013;87:8638–50.
Figures
Tables
Suggested citation for this article: Lau SKP, Wong ACP, Luk HKH, Li KSM, Fung J, He Z, et al. Differential tropism of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 in bat cells. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Dec [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2612.202308
1These authors contributed equally to this article.





















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario