
Volume 25, Number 9—September 2019
Etymologia
Etymologia: Sporothrix schenckii
Figures
Downloads
Article Metrics
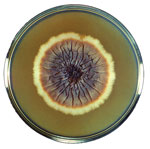
From the Greek sporotrich and later from the Latin spor- (spore) + thrix (hair), Sporothrix schenckii was named as a tribute to Benjamin Schenck, a medical student at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, who first isolated the fungus from a patient who had lesions on the right hand and arm in 1896 (Figure). This fungus was erroneously assigned to the genus Sporotrichum until 1962, when it was reclassified as Sporothrix.
S. schenckii is a saprophyte and pathogenic fungus that is responsible for sporotrichosis that is endemic mostly to tropical and subtropical regions. Sporotrichosis (also known as “rose gardener’s disease”) was related primarily to agricultural workers who had cuts or abrasions in the skin, and later to scratches and bites from companion and wild animals. Currently, it is recognized that S. schenckii is a species complex that includes S. brasiliensis, S. globosa, S. mexicana, S. luriei, and S. schenckii sensu stricto.
References
- Barros MB, de Almeida Paes R, Schubach AO. Sporothrix schenckii and Sporotrichosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:633–54.
- Gold JA, Derado G, Mody RK, Benedict K. Sporotrichosis-Associated Hospitalizations, United States, 2000-2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22:1817–20.
- Marimon R, Cano J, Gené J, Sutton DA, Kawasaki M, Guarro J. Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, three new Sporothrix species of clinical interest. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3198–206.
- Schenck BR. On refractory subcutaneous abscess caused by a fungus possibly related to the Sporotricha. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1898;9:286–90.
- Schubach A, Schubach TM, Barros MB, Wanke B. Cat-transmitted sporotrichosis, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1952–4.
Figure
Cite This ArticleOriginal Publication Date: 7/30/2019





















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario