Volume 25, Number 9—September 2019
Synopsis
Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes for Patients Infected with Mycobacterium haemophilum
On This Page
Tables
Downloads
Article Metrics
Abstract
Mycobacterium haemophilum is a nontuberculous mycobacterium that can infect immunocompromised patients. Because of special conditions required for its culture, this bacterium is rarely reported and there are scarce data for long-term outcomes. We conducted a retrospective study at Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand, during January 2012–September 2017. We studied 21 patients for which HIV infection was the most common concurrent condition. Most common organ involvement was skin and soft tissue (60%). Combination therapy with macrolides and fluoroquinolones resulted in a 60% cure rate for cutaneous infection; adding rifampin as a third drug for more severe cases resulted in modest (66%) cure rate. Efficacy of medical therapy in cutaneous, musculoskeletal and ocular diseases was 80%, 50%, and 50%, respectively. All patients with central nervous system involvement showed treatment failures. Infections with M. haemophilum in HIV-infected patients were more likely to have central nervous system involvement and tended to have disseminated infections and less favorable outcomes.
Mycobacterium haemophilum is a nontuberculous mycobacterium that causes localized and disseminated infections in immunocompromised patients and rarely in immunocompetent patients (1). It is a slow-growing, aerobic, fastidious mycobacterium that requires heme-supplemented culture medium and low temperatures of 30°C–32°C for optimal growth (2). Because of the special conditions required for culture, it is frequently not isolated because of use of inappropriate techniques, and thus rarely reported in the medical literature.
The most common clinical manifestation of infection in adult patients is cutaneous disease (3,4), either localized or as part of disseminated disease that occurs mainly in severely immunocompromised patients, such as those infected with HIV, those with autoimmune disease, or those who have undergone solid organ or stem cell transplantation (5–10). Thus, infection with M. hemophilum should be suspected in immunocompromised patients who have unexplained skin lesions and are smear positive for acid-fast bacilli, but show negative results for routine mycobacterial culture.
There is no current standardized guideline for optimal management for patients infected with M. haemophilum. Furthermore, the long-term outcome of this infection has not been well documented. The purpose of this study was to determine clinical characteristics, treatment, and long-term outcomes for infections with M. haemophilum.
We conducted a retrospective cohort study at Siriraj Hospital, the largest academic hospital in Bangkok, Thailand, during January 2012–September 2017. We identified all patients who were given a diagnosis of M. haemophilum infection by culture or molecular methods. Specimens of all types underwent smear microscopic analysis by using auramine–rhodamine staining and mycobacterial culture by using Lowenstein-Jensen solid medium and liquid medium containing mycobacteria growth indicator. All specimens were incubated at 35°C, and those from skin, bone, and joint were also incubated at 30°C. We performed species identification by using the INNO-LiPA Mycobacteria Version 2 Assay (Innogenetics [now Fujiregio], ). We reviewed baseline demographics, clinical characteristics, microbiological data, antimicrobial and surgical treatment, and clinical outcome. All patients were followed-up for >1 year after diagnosis. This study was approved by the institutional review board committee at Siriraj Hospital (Chart of Accounts no. Si 630/2017).
A total of 21 patients were included in this study; 67% were women (median age 53 years, range 25–73 years). All 21 patients were immunocompromised. The most common concurrent condition was HIV infection (8 patients, 38%), followed by systemic lupus erythematosus (5 patients, 23.8%), γ-interferon autoantibody (2 patients, 9.5%), kidney transplantation (2 patients, 9.5%), diabetes mellitus (2 patients, 9.5%), ankylosing spondylitis (1 patient), and nephrotic syndrome (1 patient).
All HIV-infected patients except 1 had CD4 cell counts <200 cells/mm3. Among non–HIV-infected patients, those with systemic lupus erythematosus, kidney transplantation, and nephrotic syndrome received corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive agents.
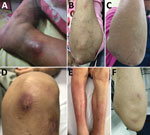
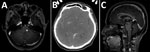
The most common organ involved was skin and soft tissue (13 patients), followed by bone and joint (3 patients), central nervous system (CNS) (3 patients), eye (2 patients), and lymph nodes (1 patient). Two patients (1 with CNS involvement [no. 1] and 1 with bone and joint infection [no. 14)]) had concomitant mycobacteremia. The most common cutaneous manifestation was an erythematous nodule that commonly occurred on the extensor surface of elbows, legs, and the auricular area (Figure 1). Of 7 skin biopsy specimens, granulomatous inflammation was the most common pathologic finding. Three patients who had CNS involvement had advanced HIV disease and CD4 cell counts <50 cells/mm3. We obtained computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging findings for 3 patients with CNS involvement (Figure 2).
We did not perform antimicrobial drug susceptibility testing on any bacterial isolate because of a failure of growth in solid medium A total of 20/21 patients were treated with a combination of antimycobacterial agents. For 19 patients whose outcomes were available, 11 patients were cured, 1 patient improved with ongoing antimicrobial drug treatment, 3 patients required surgical excision after failure of medical therapy, 3 patients had a relapse of their infection after treatment discontinuation, and 1 patient died from disseminated disease after 1 month of therapy (Table).
The success rate of medical therapy for cutaneous infection was 80%. However, this rate was lower (50%) for bone, joint, and ocular infections. All patients with CNS diseases and involvement showed treatment failures.
The most commonly used regimen included a combination of macrolides and fluoroquinolones (3 patients, 14.3%) or these combined regimens with rifampin (9 patients, 42.9%). Combination therapy with macrolides and fluoroquinolones resulted in a success rate of 60% for treatment of cutaneous infection. Use of rifampin as the third drug for more severe cases also resulted in a modest (66%) success rate. Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, doxycycline, and cycloserine were also replaced with rifampin, which showed clinically successful results. For 11 patients in whom antimicrobial drugs could be discontinued, the median duration of treatment was 12 months (range 3–12 months for skin and soft tissue infections, 6 months for bone and joint infections, and 12 months for lymphadenitis and eye infections).
The patient who died of disseminated M. haemophilum infection was a 25-year-old man who was given a new diagnosis of infection with HIV and had a CD4 cell count of 17 cells/mm3. He had diplopia for 1 month and a low-grade fever. Physical examination showed multiple left-sided cranial nerve palsies (V [trigeminal], VI [abducens], and VII [facial]), lower motor neuron lesions. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain showed multiple, abnormal, high-signal intensity lesions on T2-weighted imaging with gadolinium, as well as nodular enhancement of the left dorsal pons, right ventral pons, mid pons, left cerebellar peduncle, and medulla (Figure 2, panel A). Examination of cerebrospinal fluid showed standard results, hemoculture grew M. haemophilum. He was given levofloxacin, azithromycin, and ethambutol. However, his clinical condition deteriorated rapidly. Right hemiparesis then developed and he became stuporous. He died from acute respiratory failure secondary to aspiration pneumonia.
When we compared HIV-infected and non–HIV infected patients, HIV-infected patients were younger (median age 36 years vs. 57 years; p = 0.017), more likely to have disseminated infection (37.5% vs. 15.4%; p = 0.325), more likely to have CNS involvement (37.5% vs. 0%; p = 0.042), and more likely to have a less favorable prognosis (50% vs. 77%; p = 0.38).
We report 21 cases of M. haemophilum infection over a 6-year period at the largest academic hospital in Thailand. M. haemophilumcommonly causes infection in immunocompromised persons. Advanced HIV infection remains the most common immunocompromised condition associated with this infection, as reported (1,3). Approximately 60% of patients have skin and soft tissue involvement, and the most commonly involved areas are the extensor surfaces of the extremities and auricular regions, which could be explained by the predilection of the organism for body areas with lower temperatures.
Although CNS infection with M. haemophilum is extremely rare and only a few case-patients have been reported (11–13), we identified CNS involvement in 3 of 21 case-patients in our study. All had advanced HIV disease: 2 patients had multiple brain abscesses, which was similar to those previously described, and 1 patient had myelitis. A total of 2 of 3 previous case reports of CNS involvement in patients with M. haemophilum infection were from Thailand and in HIV-infected patients (11,12), whereas the 2 largest case series (23 and 15 cases) reported from the United States found no cases of CNS involvement (3,4). Further study is needed to determine whether genetic or environmental factors will influence clinical manifestations of M. haemophilum infection.
Treatment with a combination of fluoroquinolones, rifampin, and macrolides is suggested for treating M. haemophilum infection (14). However, our study demonstrated that 2 antimycobacterial agents (macrolides and fluoroquinolones) were successfully used for patients with isolated cutaneous diseases. Conversely, surgical resection might be needed for some case-patients, such as those who showed treatment failure or those in which there was CNS involvement. Because of poor penetration of the CNS by these antimicrobial agents, patients who had mycobacterial infections with CNS involvement are often associated with poorer outcomes (15,16). Two previous case reports of persons with CNS disease were successfully treated with surgical excision in combination with antimicrobial drugs, although there were residual neurologic deficits (11,13). Another study reported a case-patient who did not respond to medical therapy alone and subsequently died (12).
Treatment for M. haemophilum infection should last ≈3–12 months and should be tailored on the basis of severity of disease and immunocompromised conditions. Isolated cutaneous disease usually responds well to shorter duration of therapy (3–6 months), and CNS infections, bone and joint infections, and disseminated disease usually require longer therapy (12 months) (1). Relapse cases have been rarely reported (17), and accounted for just 4% in the largest case series (1). However, our study showed a higher relapse rate (14%); therefore, we suggest that careful monitoring after discontinuation of treatment is warranted.
One limitation of our study was that no antimicrobial susceptibility testing was available because all culture-positive cases were detected in liquid medium. However, no data support the correlation of in vitro susceptibility testing and treatment response for this type of infection.
M. haemophilum infections should be suspected in immunocompromised patients who have unexplained cutaneous lesions, especially at auricular or extensor surfaces of extremities, who are smear positive for acid-fast bacilli, but show negative results for routine mycobacterial culture. Combination antimycobacterial therapy should be given for >3 months and extended to 12 months depending on the site of isolation. CNS involvement might occur more commonly than previously believed and is associated with worse outcome. Relapses are not uncommon; therefore, clinical monitoring after discontinuation of treatment is warranted.
Dr. Nookeu is a physician in the Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand. Her primary research interest is nontuberculous mycobacteria.
Acknowledgment
We thank all medical staff and laboratory technicians who were involved in the study and those who cared for the patients.
References
- Lindeboom JA, Bruijnesteijn van Coppenraet LE, van Soolingen D, Prins JM, Kuijper EJ. Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of Mycobacterium haemophilum infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:701–17.
- Dawson DJ, Jennis F. Mycobacteria with a growth requirement for ferric ammonium citrate, identified as Mycobacterium haemophilum. J Clin Microbiol. 1980;11:190–2.
- Shah MK, Sebti A, Kiehn TE, Massarella SA, Sepkowitz KA. Mycobacterium haemophilum in immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:330–7.
- Tyner HL, Wilson JW. Fifteen-year clinical experience with Mycobacterium haemophilum at the Mayo Clinic: a case series. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2017;8:26–32.
- Kelley CF, Armstrong WS, Eaton ME. Disseminated Mycobacterium haemophilum infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011;11:571–8.
- Brix SR, Iking-Konert C, Stahl RA, Wenzel U. Disseminated Mycobacterium haemophilum infection in a renal transplant recipient. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:
bcr2016216042 . - Jacobs SE, Zhong E, Hartono C, Satlin MJ, Magro CM, Jenkins SG, et al. The brief case: disseminated Mycobacterium haemophiluminfection in a kidney transplant recipient. J Clin Microbiol. 2017;56:e00561–17.
- Otome O, O’Reilly M, Lim L. Disseminated Mycobacterium haemophilum skeletal disease in a patient with interferon-gamma deficiency. Intern Med J. 2015;45:1073–6.
- Brissot E, Gomez A, Aline-Fardin A, Lalande V, Lapusan S, Isnard F, et al. Report of disseminated Mycobacterium haemophiluminfection after double cord blood allo-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:1347–8.
- Collins CS, Terrell C, Mueller P. Disseminated Mycobacterium haemophilum infection in a 72-year-old patient with rheumatoid arthritis on infliximab. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013(mar15 1):
bcr2012008034 . - Phowthongkum P, Puengchitprapai A, Udomsantisook N, Tumwasorn S, Suankratay C. Spindle cell pseudotumor of the brain associated with Mycobacterium haemophilum and Mycobacterium simiae mixed infection in a patient with AIDS: the first case report.Int J Infect Dis. 2008;12:421–4.
- Buppajarntham A, Apisarnthanarak A, Rutjanawech S, Khawcharoenporn T. Central nervous system infection due to Mycobacterium haemophilum in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Int J STD AIDS. 2015;26:288–90.
- Barr LK, Sharer LR, Khadka Kunwar E, Kapila R, Zaki SR, Drew CP, et al. Intraventricular granulomatous mass associated with Mycobacterium haemophilum: A rare central nervous system manifestation in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection.J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22:1057–60.
- Medical Section of the American Lung Association. Diagnosis and treatment of disease caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria. This official statement of the American Thoracic Society was approved by the Board of Directors, March 1997. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156:S1–25.
- Jacob CN, Henein SS, Heurich AE, Kamholz S. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infection of the central nervous system in patients with AIDS. South Med J. 1993;86:638–40.
- Lee MR, Cheng A, Lee YC, Yang CY, Lai CC, Huang YT, et al. CNS infections caused by Mycobacterium abscessus complex: clinical features and antimicrobial susceptibilities of isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67:222–5.
- Ducharlet K, Murphy C, Tan SJ, Dwyer KM, Goodman D, Aboltins C, et al. Recurrent Mycobacterium haemophilum in a renal transplant recipient. Nephrology (Carlton). 2014;19(Suppl 1):14–7.
Figures
Table
Suggested citation for this article: Nookeu P, Angkasekwinai N, Foongladda S, Phoompoung P. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes for patients infected with Mycobacterium haemophilum. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 Sep [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2509.190430
Original Publication Date: 8/2/2019


































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario