Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient Version
General Information About Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia
KEY POINTS
- Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets.
- Leukemia may affect red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- There are different subtypes of AML.
- Smoking, previous chemotherapy treatment, and exposure to radiation may affect the risk of adult AML.
- Signs and symptoms of adult AML include fever, feeling tired, and easy bruising or bleeding.
- Tests that examine the blood and bone marrow are used to diagnose adult AML.
- Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets.
Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated. It is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. AML is also called acute myelogenous leukemia, acute myeloblastic leukemia, acute granulocytic leukemia, and acute nonlymphocytic leukemia.
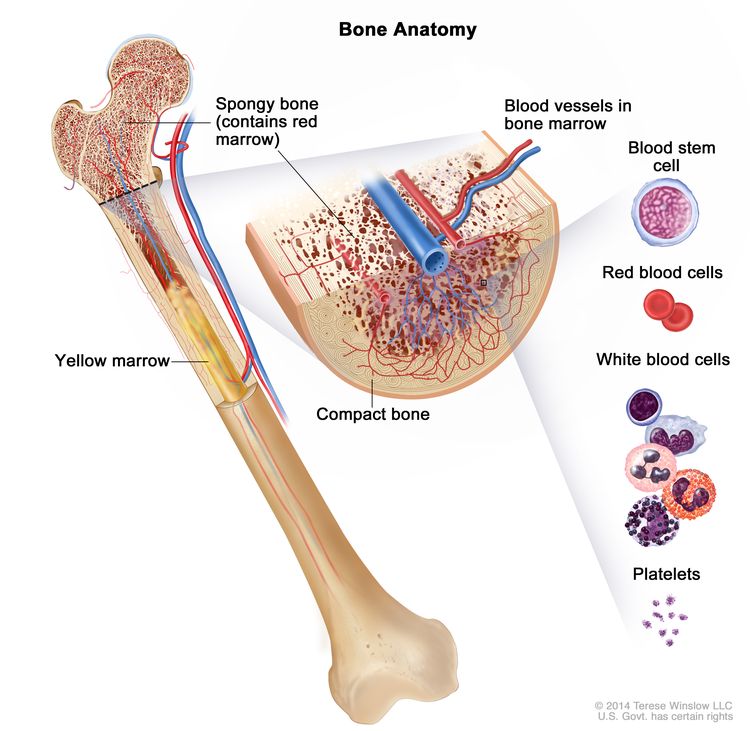
Leukemia may affect red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Normally, the bone marrow makes blood stem cells (immature cells) that become mature blood cells over time. A blood stem cell may become a myeloid stem cell or a lymphoid stem cell. A lymphoid stem cell becomes a white blood cell.
A myeloid stem cell becomes one of three types of mature blood cells:
- Red blood cells that carry oxygen and other substances to all tissues of the body.
- White blood cells that fight infection and disease.
- Platelets that form blood clots to stop bleeding.
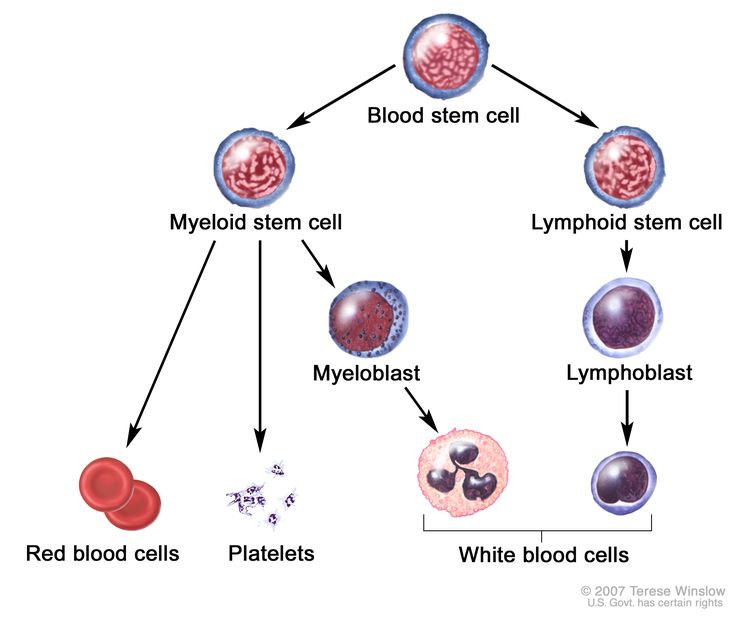
In AML, the myeloid stem cells usually become a type of immature white blood cell called myeloblasts (or myeloid blasts). The myeloblasts in AML are abnormal and do not become healthy white blood cells. Sometimes in AML, too many stem cells become abnormal red blood cells or platelets. These abnormal white blood cells, red blood cells, or platelets are also called leukemia cells or blasts. Leukemia cells can build up in the bone marrow and blood so there is less room for healthy white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. When this happens, infection, anemia, or easy bleeding may occur. The leukemia cells can spread outside the blood to other parts of the body, including the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), skin, and gums.
This summary is about adult AML. See the following PDQ summaries for information about other types of leukemia:





















.png)












No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario